Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2017; 23(37): 6833-6844
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6833
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6833
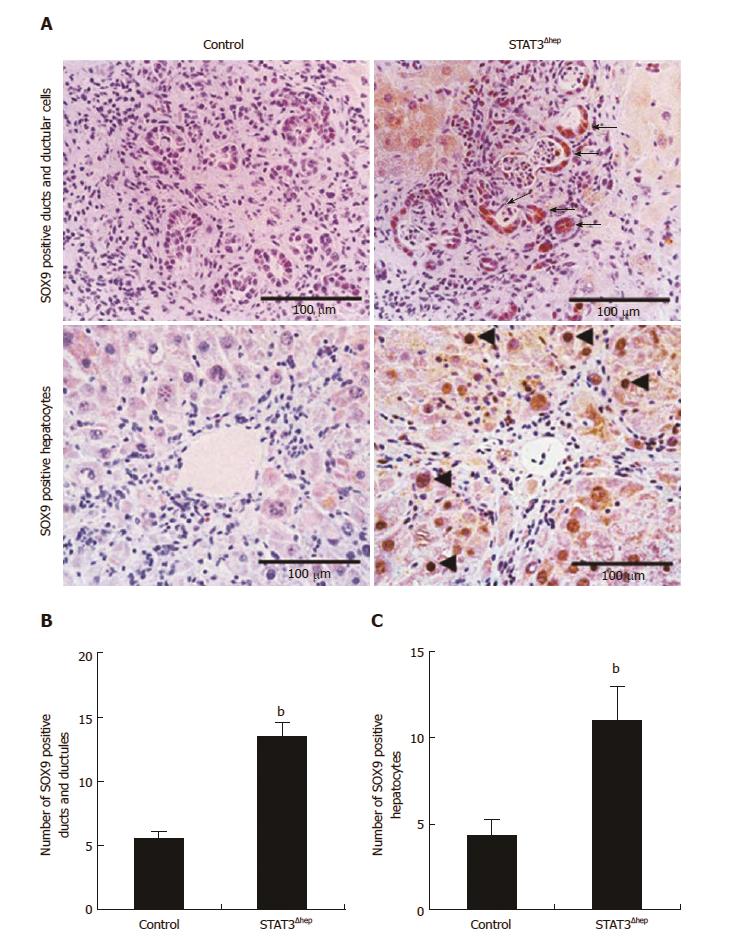
Figure 4 Hepatic STAT3 deficiency upregulated SOX9 expression in thioacetamide-induced liver injury.
A: Immunohistochemistry staining for SOX9 in control and STAT3Δhep livers with TAA treatment for 16 wk. SOX9 expression was markedly enhanced in bile ducts/ductular structure (upper panel) and hepatocytes (lower panel) of STAT3Δhep livers. Original magnification × 200 (upper panel) and × 400 (lower panel). B and C: The number of SOX9 positive bile ducts/ductular structure and hepatocytes. For quantification of SOX9 positive bile ducts/ductular structure, three different samples per a group were observed using a 20 × objective lens and SOX9 positive ducts/ductular structure was counted at five PV areas. For quantification of SOX9 positive hepatocytes, three different samples per a group were observed using a 40 × objective lens and SOX9 positive hepatocytes was counted at five PV areas. Values represent means ± standard error of the mean. bP < 0.01 [(B) P = 0.0000103, (C) P = 0.00834] vs control. TAA: Thioacetamide.
- Citation: Abe M, Yoshida T, Akiba J, Ikezono Y, Wada F, Masuda A, Sakaue T, Tanaka T, Iwamoto H, Nakamura T, Sata M, Koga H, Yoshimura A, Torimura T. STAT3 deficiency prevents hepatocarcinogenesis and promotes biliary proliferation in thioacetamide-induced liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(37): 6833-6844
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i37/6833.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6833