Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2017; 23(37): 6777-6787
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6777
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6777
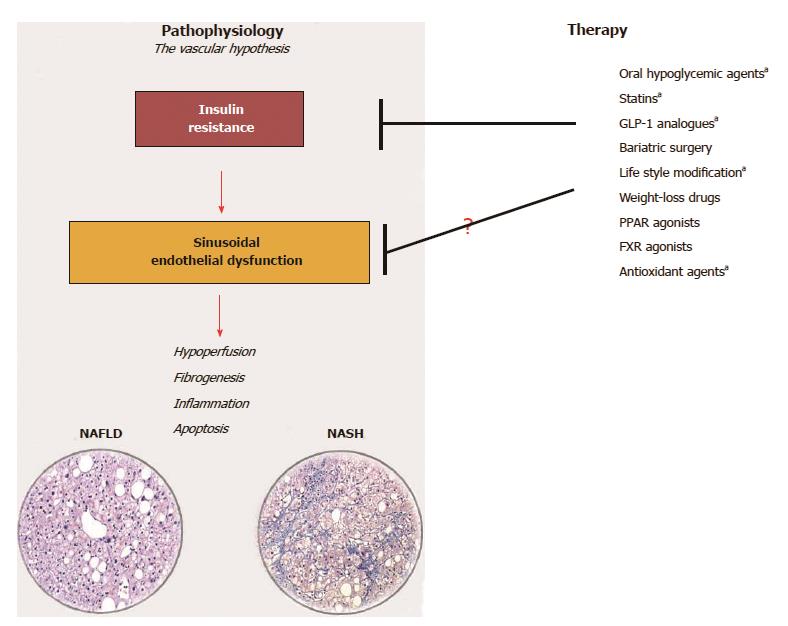
Figure 3 The vascular-hypothesis of liver damage in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease considers sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction due to insulin-resistance a key factor for the initiation and perpetuation of liver damage from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis.
Any strategy of treatment ameliorating insulin-resistance may be efficacious in ameliorating sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction. Drugs marked with a are those with a proven efficacy on liver microcirculation (Ref. [16,42,95,103,104]). (Histological images are courtesy of Dr. Marco Maggioni, IRCCS Ca’ Granda, Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, Italy). NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Pasarín M, Abraldes JG, Liguori E, Kok B, La Mura V. Intrahepatic vascular changes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Potential role of insulin-resistance and endothelial dysfunction. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(37): 6777-6787
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i37/6777.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6777