Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2017; 23(37): 6777-6787
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6777
Published online Oct 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6777
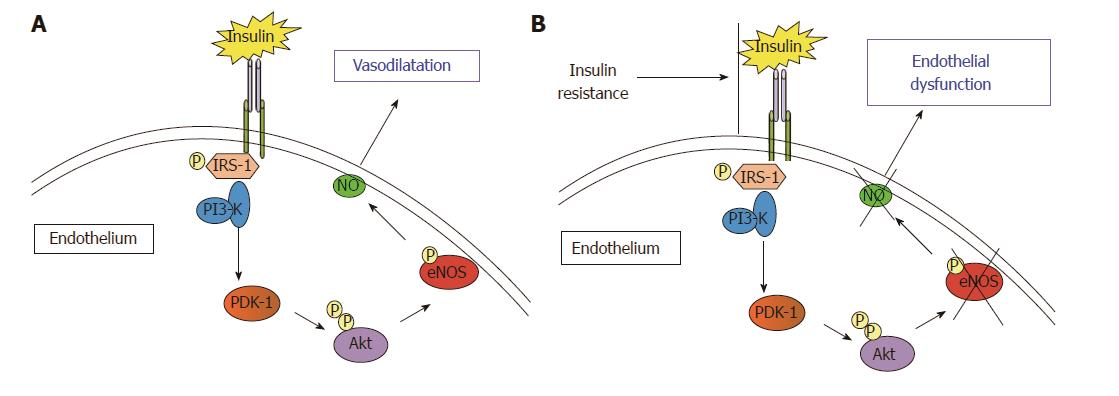
Figure 1 The binding of insulin to its receptor activates a series of phosphorylations of downstream receptors that finally activate nitric oxide-production by endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
A: The release of nitric oxide (NO) causes endothelium dependent vasodilation; B: Insulin-resistance causes the reduction of Insulin-induced activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). This is associated with reduction of NO bioavailability and, finally, endothelial dysfunction.
- Citation: Pasarín M, Abraldes JG, Liguori E, Kok B, La Mura V. Intrahepatic vascular changes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Potential role of insulin-resistance and endothelial dysfunction. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(37): 6777-6787
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i37/6777.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6777