Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2017; 23(36): 6705-6714
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6705
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6705
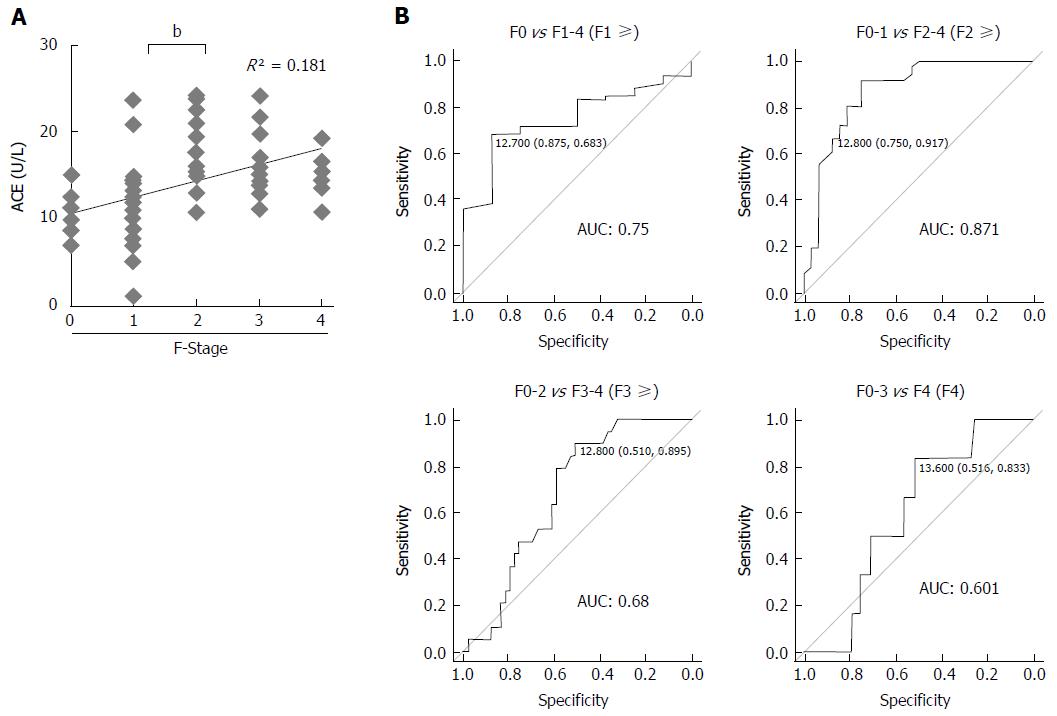
Figure 3 Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme levels and liver fibrosis development in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
A: Correlation between serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) level and liver fibrosis stage (F-Stage) (R = 0.42, R2 = 0.181); B: Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis and area under curve (AUC) value for diagnostic performance of serum ACE level for predicting each stage of liver fibrosis. The optimal ACE level cut-off point for significant fibrosis was 12.8 U/L. Data are means ± SD, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Noguchi R, Kaji K, Namisaki T, Moriya K, Kitade M, Takeda K, Kawaratani H, Okura Y, Aihara Y, Furukawa M, Mitoro A, Yoshiji H. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level for evaluating significant fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(36): 6705-6714
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i36/6705.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6705