Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2017; 23(36): 6650-6664
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6650
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6650
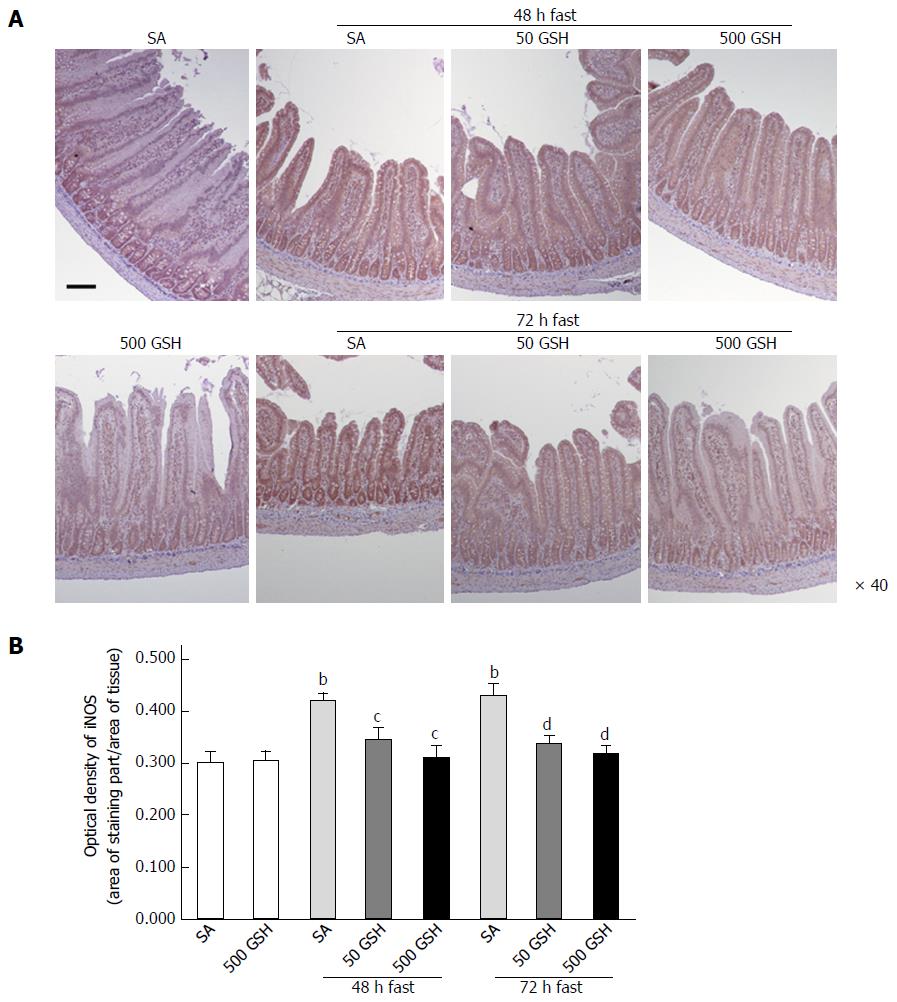
Figure 4 Effects of fasting and glutathione treatment on inducible nitric oxide synthase protein expression in the jejunum.
A: Light micrographs of immunohistochemical staining for iNOS. In SA-treated groups, iNOS protein staining was localized almost exclusively in the mucosal epithelial monolayer with 48 and 72 h of fasting compared with the normally fed control. Decreased staining occurred with GSH treatment. Bar = 100 μm. B: Optical density of iNOS protein. The content of iNOS protein was quantitatively measured by averaging the optical density. Values represent the mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs normally fed controls. dP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 vs the respective SA group in each fasting period. 7-8 rats were tested in each group. GSH: Glutathione; SA: Saline; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
- Citation: Uchida H, Nakajima Y, Ohtake K, Ito J, Morita M, Kamimura A, Kobayashi J. Protective effects of oral glutathione on fasting-induced intestinal atrophy through oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(36): 6650-6664
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i36/6650.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6650