Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2017; 23(36): 6571-6592
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6571
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6571
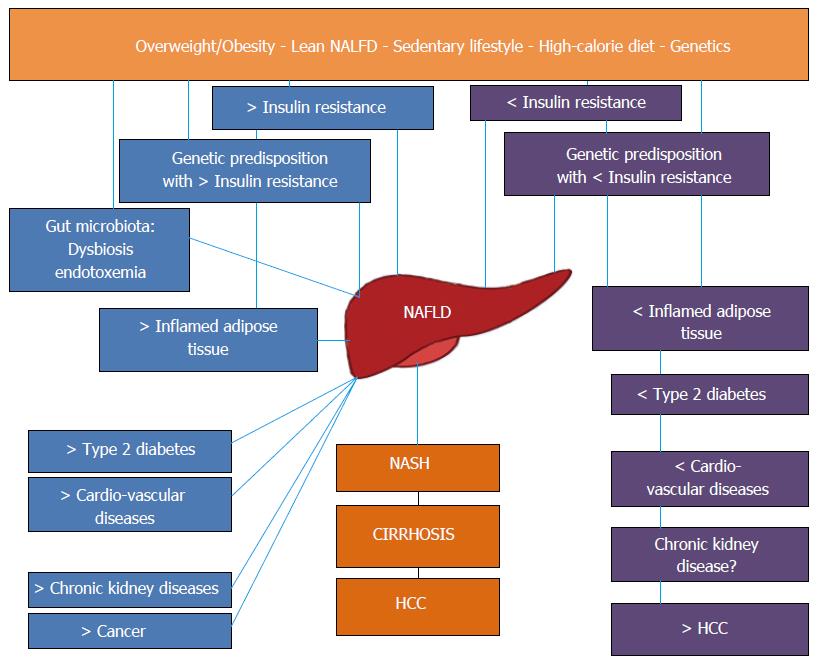
Figure 1 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a pathogenically and clinically heterogeneous condition.
Schematic representation of the pathogenic and clinical heterogeneity of different NAFLD populations. Left: “Metabolic” NAFLD is associated with adipose tissue dysfunction and IR and may progress towards hepatic and extrahepatic complications. Right: “Genetic” NAFLD seems to be disconnected from adipose tissue dysfunction and IR, is associated with an increased risk of liver disease progression but is probably spared from extrahepatic complications. NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Lonardo A, Nascimbeni F, Maurantonio M, Marrazzo A, Rinaldi L, Adinolfi LE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Evolving paradigms. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(36): 6571-6592
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i36/6571.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6571