Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2017; 23(34): 6306-6314
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6306
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6306
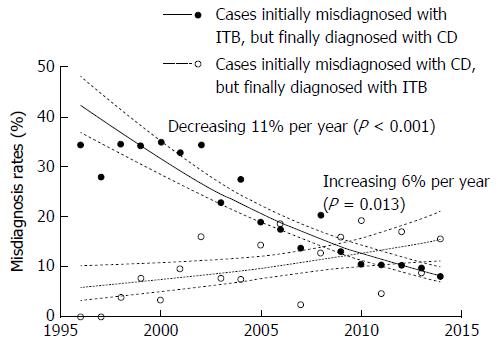
Figure 1 Temporal trends in the misdiagnosis rates between Crohn’s disease and intestinal tuberculosis during the study period.
Dots represent the observed misdiagnosis rates; lines represent the expected misdiagnosis rates and 95%CI according to the logistic regression analysis. The misdiagnosing rate of Crohn’s disease (CD) as intestinal tuberculosis (ITB) decreased to 0.89 (95%CI: 0.87-0.91) fold per year (P < 0.001); The misdiagnosing rate of ITB as CD increased to 1.06 (95%CI: 1.01-1.11) fold per year (P = 0.013).
- Citation: Seo H, Lee S, So H, Kim D, Kim SO, Soh JS, Bae JH, Lee SH, Hwang SW, Park SH, Yang DH, Kim KJ, Byeon JS, Myung SJ, Yang SK, Ye BD. Temporal trends in the misdiagnosis rates between Crohn’s disease and intestinal tuberculosis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(34): 6306-6314
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i34/6306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6306