Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2017; 23(34): 6252-6260
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6252
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6252
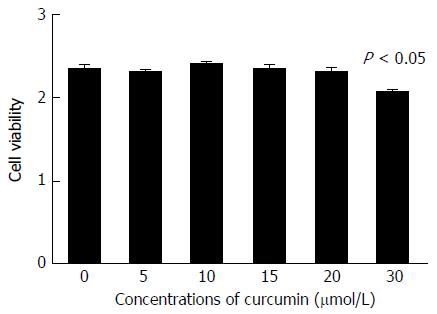
Figure 1 Cell cytotoxicity of curcumin.
HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 or 30 μmol/L curcumin for 2 d and then subjected to CCK-8 assay to detect toxic effect. The experiment was performed in duplicate and repeated at least three times.
- Citation: Wei ZQ, Zhang YH, Ke CZ, Chen HX, Ren P, He YL, Hu P, Ma DQ, Luo J, Meng ZJ. Curcumin inhibits hepatitis B virus infection by down-regulating cccDNA-bound histone acetylation. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(34): 6252-6260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i34/6252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6252