Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2017; 23(34): 6242-6251
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6242
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6242
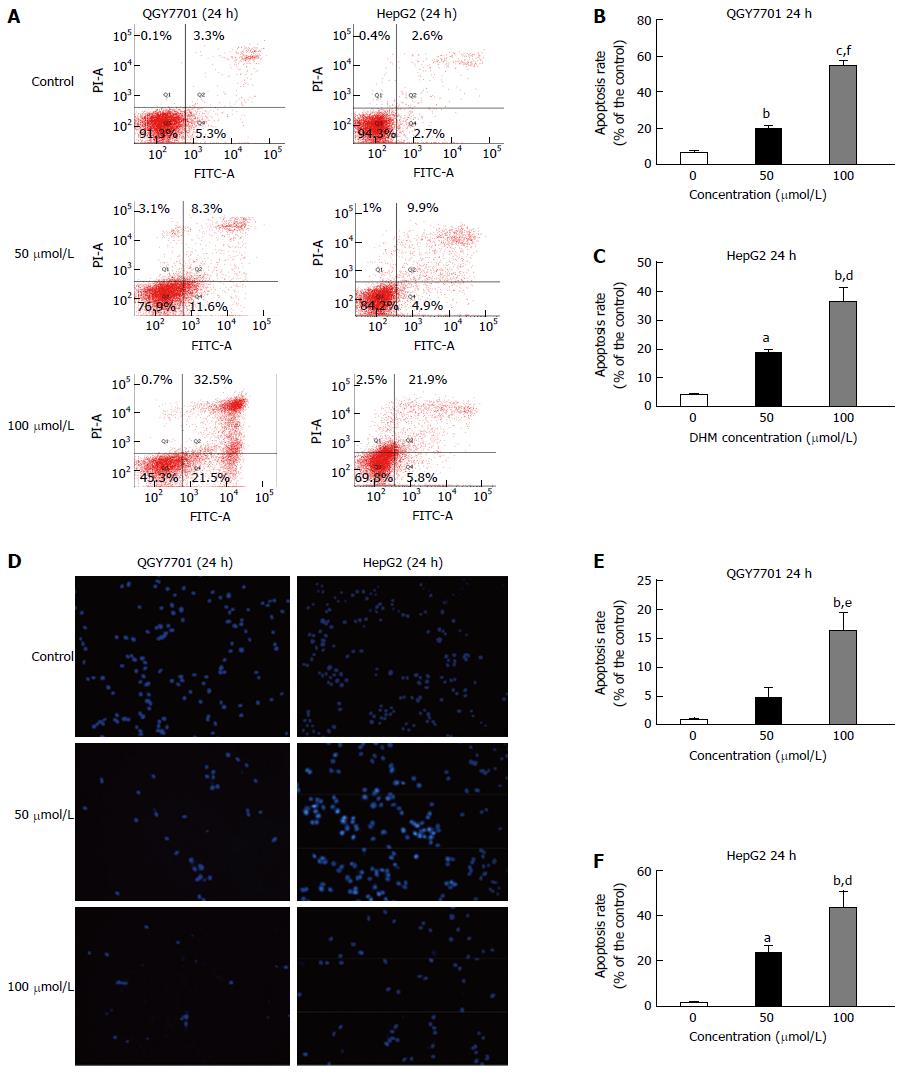
Figure 3 Dihydromyricetin induces apoptosis in QGY7701 and HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Apoptosis of QGY7701 and HepG2 cells treated with DHM at different concentrations (0, 50, or 100 μmol/L) for 24 h was analyzed by flow cytometry; B and C: Apoptosis was quantified and presented as a statistical figure; D: A TUNEL assay was utilized to examine the apoptosis of QGY7701 and HepG2 cells treated with different concentrations (0, 50, or 100 μmol/L) of DHM for 24 h; E and F: Apoptosis was quantified and presented as a statistical figure; Each experiment was repeated more than three times; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs 0 μmol/L (control) group; eP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs 50 μmol/L group.
- Citation: Lu CJ, He YF, Yuan WZ, Xiang LJ, Zhang J, Liang YR, Duan J, He YH, Li MY. Dihydromyricetin-mediated inhibition of the Notch1 pathway induces apoptosis in QGY7701 and HepG2 hepatoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(34): 6242-6251
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i34/6242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6242