Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2017; 23(34): 6220-6230
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6220
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6220
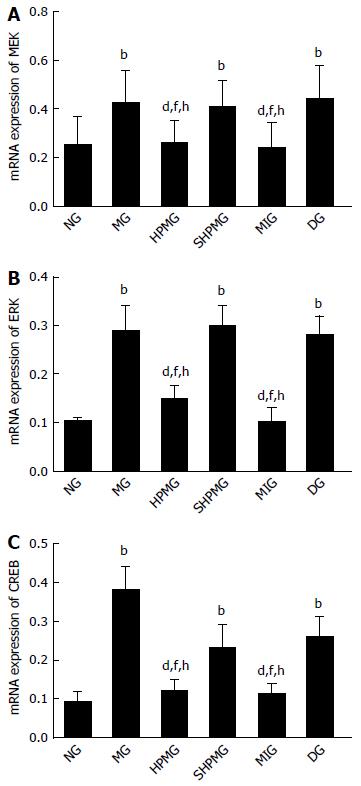
Figure 6 Comparison of expression of mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase and cAMP response element binding protein mRNAs in rat spinal cord.
A: mRNA expression of MEK; B: mRNA expression of ERK; C: mRNA expression of CREB. bP < 0.01 vs normal group; dP < 0.01 vs model group; fP < 0.01 vs sham-HPM group; hP < 0.01 vs DMSO group. CREB: cAMP response element binding protein; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; HPM: Herb-partitioned moxibustion; MEK: Mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NG: Normal group; MG: Model group; SHPMG: Sham-HPM group; MIG: MEK-inhibitor group; DG: Dimethyl sulfoxide group.
- Citation: Li ZY, Huang Y, Yang YT, Zhang D, Zhao Y, Hong J, Liu J, Wu LJ, Zhang CH, Wu HG, Zhang J, Ma XP. Moxibustion eases chronic inflammatory visceral pain through regulating MEK, ERK and CREB in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(34): 6220-6230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i34/6220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6220