Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2017; 23(33): 6100-6110
Published online Sep 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6100
Published online Sep 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6100
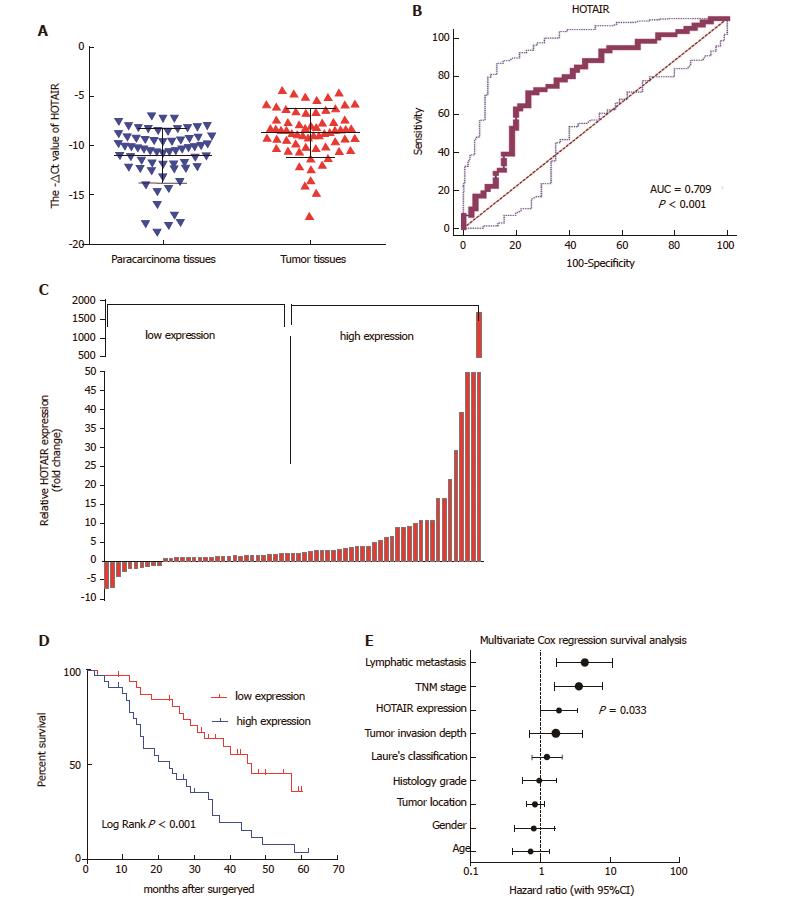
Figure 1 HOTAIR up-regulation correlates with poor survival in patients with GC.
A: HOTAIR expression was significantly up-regulated in tumor tissues compared with their corresponding para-carcinoma tissues (shown as -ΔCt); B: ROC curves for observing the diagnostic value of HOTAIR; C: HOTAIR expression was classified into two groups according to HOTAIR expression levels (median split); D: Kaplan-Meier analysis of OS was analyzed according to HOTAIR expression levels; E: Different factors (including HOTAIR, tumor invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage, histological grade, gender, tumor location, Lauren’s classification and age) were analyzed for their association with patient survival using Cox regression model. The hazard ratio and 95%CI are plotted for each factor. CI: Confidence interval; GC: Gastric cancer; HOTAIR: HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA; OS: Overall survival; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; TNM: Tumor-node-metastasis.
- Citation: Chen WM, Chen WD, Jiang XM, Jia XF, Wang HM, Zhang QJ, Shu YQ, Zhao HB. HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA represses E-cadherin expression by binding to EZH2 in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(33): 6100-6110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i33/6100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6100