Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2017; 23(32): 5945-5953
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5945
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5945
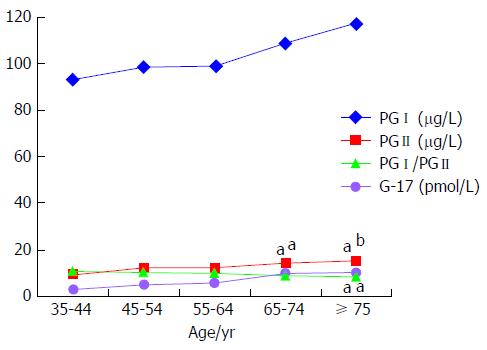
Figure 1 Comparison of serum gastric biomarker levels in various age groups.
There was no significant difference in serum levels of PGI and G-17 between each age group with increasing age. In contrast, serum levels of PGII increased with age, and were significantly higher in subjects ≥ 65-years-old compared to 35-44-years-old group. The ratio of PGI/PGII decreased with age, and was significantly lower in subjects ≥ 75-years-old compared to 35-44-years-old group. The “a” denotes comparison with 35-44-years-old age group, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. G-17: Gastrin-17; PGI: Pepsinogen I; PGII: Pepsinogen II.
- Citation: Shan JH, Bai XJ, Han LL, Yuan Y, Sun XF. Changes with aging in gastric biomarkers levels and in biochemical factors associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in asymptomatic Chinese population. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(32): 5945-5953
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i32/5945.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5945