Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2017; 23(32): 5904-5912
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5904
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5904
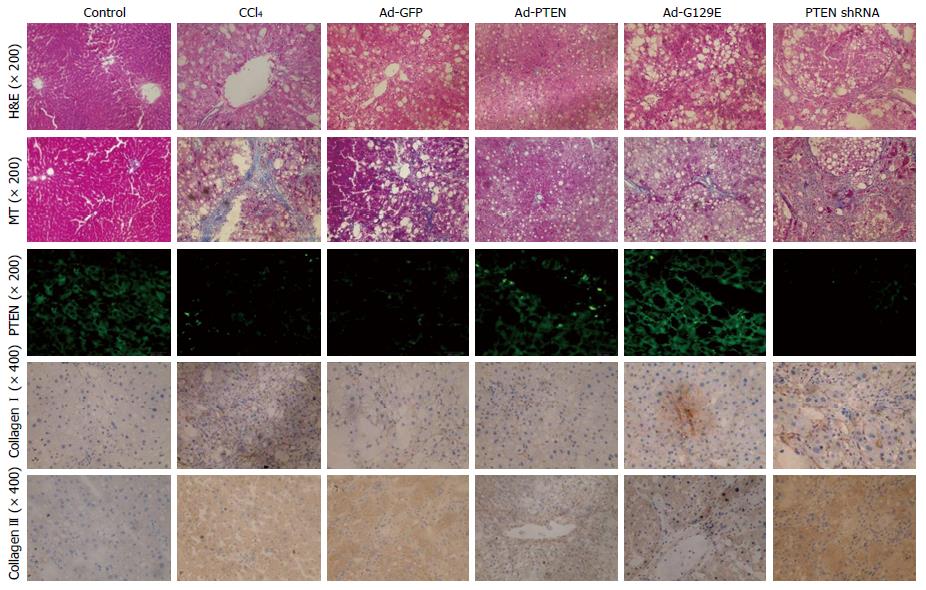
Figure 3 Phosphatase and tension homologue deleted on chromosome ten has protective effects on CCl4-induced rat hepatic fibrosis in vivo.
H&E stain (× 200) and MT stain (× 200) showed reduced hepatic cell necrosis and collagen deposition in liver tissue by over-expressed PTEN gene in Ad-PTEN and Ad-G129E groups. Immunofluorescent staining for PTEN (green) showed increased PTEN expression with Ad-PTEN and Ad-G129E recombinant adenovirus in both the prevention group or the treatment group. Immunohistochemical staining (bottom 2 rows) showed decreased collagen I and collagen III expression in hepatic tissues (× 400) with over-expression of PTEN induced by exogenous wild-type PTEN or G129E gene, whereas collagen I and collagen III expressions was reduced by PTEN shRNA. H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; MT: Masson’s trichrome; PTEN: Phosphatase and tension homologue deleted on chromosome ten.
- Citation: Xie SR, An JY, Zheng LB, Huo XX, Guo J, Shih D, Zhang XL. Effects and mechanism of adenovirus-mediated phosphatase and tension homologue deleted on chromosome ten gene on collagen deposition in rat liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(32): 5904-5912
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i32/5904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5904