Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2017; 23(32): 5895-5903
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5895
Published online Aug 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5895
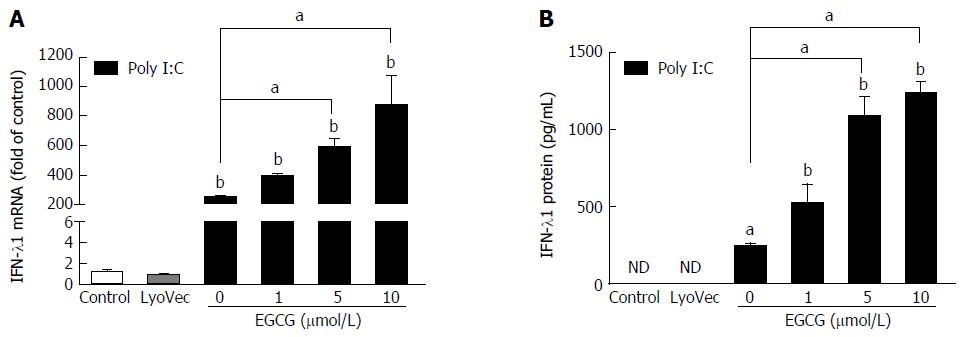
Figure 1 (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances poly I:C-induced interferon-λ1 expression in JFH-1-Huh7 cells.
JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells (72 h post-infection) were treated with EGCG at the indicated concentrations for 1 h prior to poly I:C (1 μg/mL) stimulation. Total RNA extracted from cells after 24 h of stimulation was subjected to real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for the determination of IFN-λ1 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA levels. The data are expressed as IFN-λ1 mRNA (A) levels relative (fold) to the control (vehicle only, which is defined as 1). After 48 h of stimulation, the supernatant (SN) was collected from the cell cultures for the determination of IFN-λ1 protein levels by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (B). The results shown are the mean ± SD of triplicate measurements representative of three experiments (Poly I:C vs LyoVec, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01). IFN: Interferon; EGCG: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate.
- Citation: Wang YZ, Li JL, Wang X, Zhang T, Ho WZ. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances poly I:C-induced interferon-λ1 production and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(32): 5895-5903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i32/5895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5895