Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2017; 23(31): 5700-5712
Published online Aug 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5700
Published online Aug 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5700
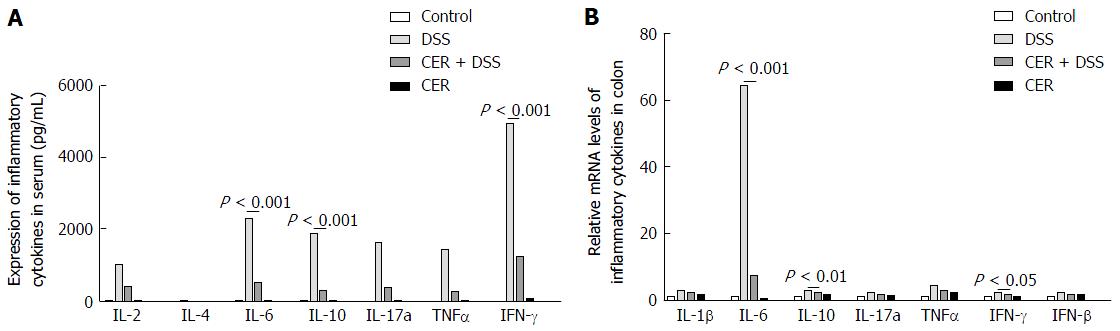
Figure 3 Administration of S.
japonicum leads to lowered inflammatory cytokines in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis mice. A: The production of IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, TNFα and IFN-γ in blood samples was detected by CBA and flow cytometry; B: IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17a, IFN-γ, TNFα and TGFβ levels in colon tissues were tested by RT-PCR. n = 3 or 4. Exposure to S. japonicum protected mice from DSS-induced colitis with down-regulation of the Th1/Th2/Th17 pathway. DSS: Dextran sodium sulfate treatment alone; CER + DSS: Infection with S. japonicum before DSS treatment; CER: S. japonicum infection alone.
- Citation: Liu Y, Ye Q, Liu YL, Kang J, Chen Y, Dong WG. Schistosoma japonicum attenuates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice via reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(31): 5700-5712
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i31/5700.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5700