Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2017; 23(31): 5680-5691
Published online Aug 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5680
Published online Aug 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5680
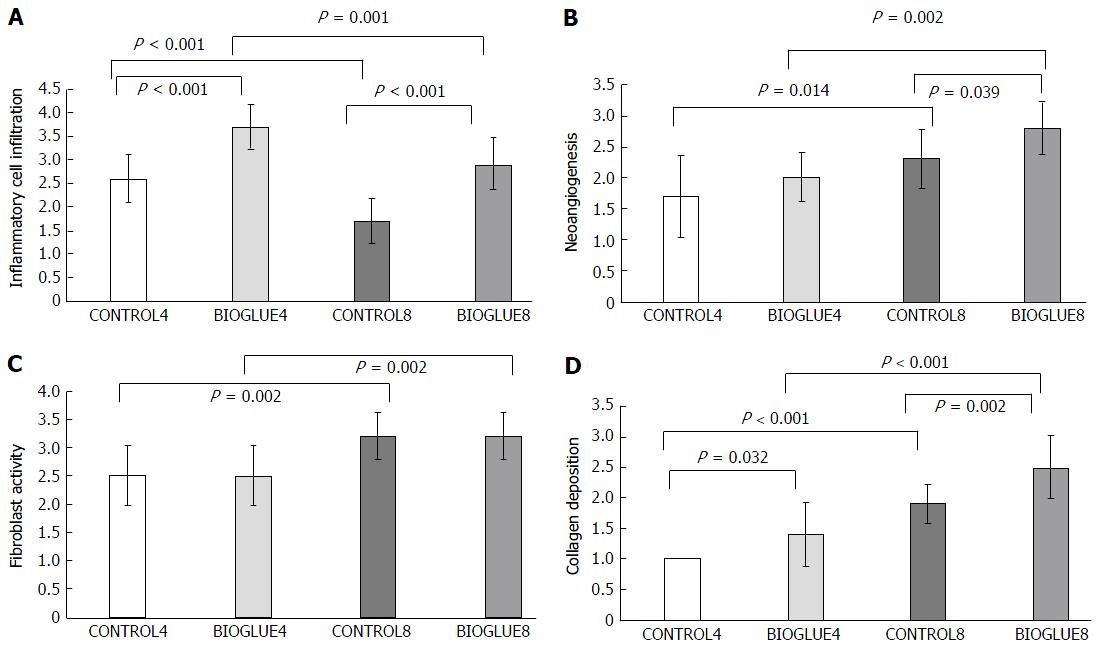
Figure 7 Comparative bar chart presenting the average inflammatory cell infiltration (A), new vessel formation (neoangiogenesis) (B), fibroblast activity (C) and collagen deposition (D), according to the scale of Ehrlich and Hunt, as modified by Phillips et al[19] (0-4) (mean ± SD).
A: The average inflammatory cell infiltration was statistically significantly higher in the Bioglue subgroups on both the fourth and eighth days than in the controls. Also, in each subgroup, there was a statistically significant decrease in the average inflammatory cell infiltration from the fourth to the eighth day; B: The average neoangiogenesis was statistically significantly higher in the Bioglue subgroups on the eighth day than in the control. Also, in each subgroup, there was a statistically significant increase in neoangiogenesis from the fourth to the eighth day; C: The average fibroblast activity was statistically significantly higher in each subgroup from the fourth to the eighth day; D: The average collagen deposition was statistically significantly higher in the Bioglue subgroups on both the fourth and eighth days than in the control. Also, in each subgroup there was a statistically significant increase in collagen deposition from the fourth to the eighth day.
- Citation: Despoudi K, Mantzoros I, Ioannidis O, Cheva A, Antoniou N, Konstantaras D, Symeonidis S, Pramateftakis MG, Kotidis E, Angelopoulos S, Tsalis K. Effects of albumin/glutaraldehyde glue on healing of colonic anastomosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(31): 5680-5691
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i31/5680.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5680