Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2017; 23(30): 5530-5537
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5530
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5530
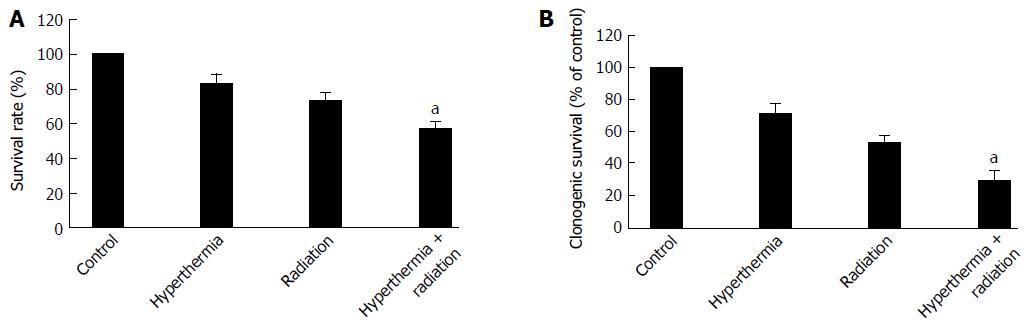
Figure 1 Hyperthermia enhances the cytotoxicity of ionizing radiation to hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
HepG2 cells were treated with hyperthermia (43 °C for 0.5 h) followed by ionizing radiation (4 Gy). After 72 h of incubation, the cells were assessed for cell viability using MTT assay (A), or plated in dishes and incubated for clonogenic survival assay (B). The results are presented as the mean ± SD of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 vs treatment of ionizing radiation alone.
- Citation: Yuan GJ, Deng JJ, Cao DD, Shi L, Chen X, Lei JJ, Xu XM. Autophagic cell death induced by reactive oxygen species is involved in hyperthermic sensitization to ionizing radiation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(30): 5530-5537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i30/5530.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5530