Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2017; 23(30): 5519-5529
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5519
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5519
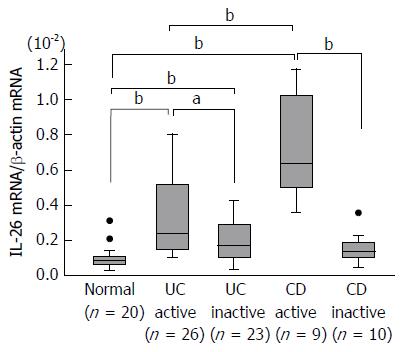
Figure 1 Expression of interleukin-26 mRNA in the inflamed mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Total RNA was extracted from biopsied samples, and the mRNA expression of IL-26 was evaluated using real-time PCR. IL-26 mRNA expression was converted to a value relative to β-actin mRNA expression and presented as fold-increase relative to the results for normal mucosa. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. Normal mucosa, n = 20; active UC, n = 26; inactive UC, n = 23; active CD, n = 9; inactive CD, n = 10. aP < 0.05 UC active vs UC inactive, bP < 0.01 Normal vs UC active, Normal vs UC inactive, Normal vs CD active, UC active vs CD active, CD active vs CD inactive. IL: Interleukin; CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Fujii M, Nishida A, Imaeda H, Ohno M, Nishino K, Sakai S, Inatomi O, Bamba S, Kawahara M, Shimizu T, Andoh A. Expression of Interleukin-26 is upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(30): 5519-5529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i30/5519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5519