Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2017; 23(30): 5499-5507
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5499
Published online Aug 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5499
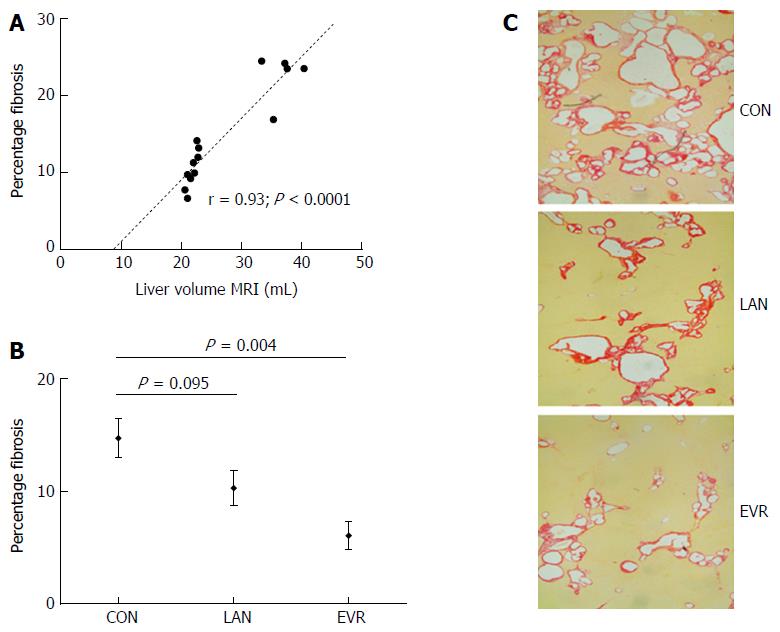
Figure 3 Liver fibrosis in PCK rats and effect of treatment with lanreotide or everolimus.
Picrosirius red collagen staining was performed on formalin fixed, paraffin embedded liver tissue, staining was assessed using Olympus Stream image analysis software 1.9 Software. Fibrosis was expressed as percentage of total liver parenchyma from 4 random selected samples per animal. A: Pearson correlation (r) and significance for liver volume with fibrosis in control animals; B: Amount of fibrosis relative to total parenchyma in the livers of PCK rats after 12 wk of treatment with LAN or EVR and in controls. Results are given as mean and SE; C: Representative images of the amount of fibrosis by picrosirius red staining in the 3 groups (original magnification × 40). CON: Control; LAN: Lanreotide; EVR: Everolimus.
- Citation: Temmerman F, Chen F, Libbrecht L, Vander Elst I, Windmolders P, Feng Y, Ni Y, De Smedt H, Nevens F, van Pelt J. Everolimus halts hepatic cystogenesis in a rodent model of polycystic-liver-disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(30): 5499-5507
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i30/5499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5499