Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2017; 23(29): 5333-5344
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5333
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5333
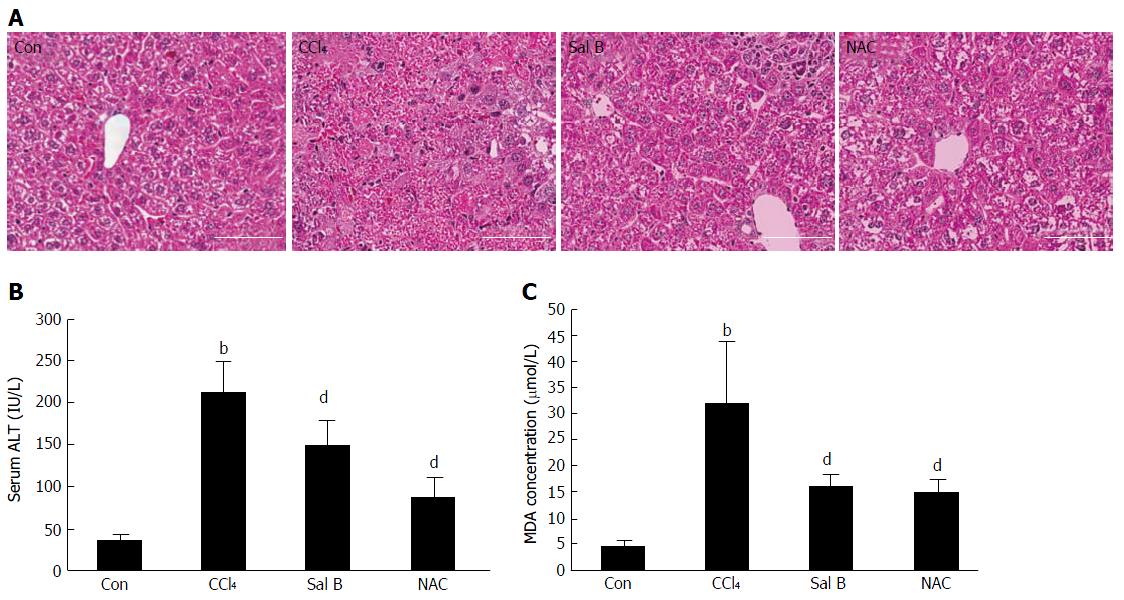
Figure 7 Effect of Sal B on CCl4-induced liver injury.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining is shown (scale bar =100 μm). Con:control group (n = 6), CCl4: CCl4 injection group (n = 6), Sal B: CCl4 injection and Sal B administration group (n = 6), NAC: CCl4 injection and NAC administration group (n = 6); B: Serum ALT activity in mice; C: MDA content of liver tissues in mice. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test (bP < 0.01 vs Con; dP < 0.01 vs CCl4). ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
- Citation: Yan XF, Zhao P, Ma DY, Jiang YL, Luo JJ, Liu L, Wang XL. Salvianolic acid B protects hepatocytes from H2O2 injury by stabilizing the lysosomal membrane. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(29): 5333-5344
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i29/5333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5333