Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2017; 23(29): 5333-5344
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5333
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5333
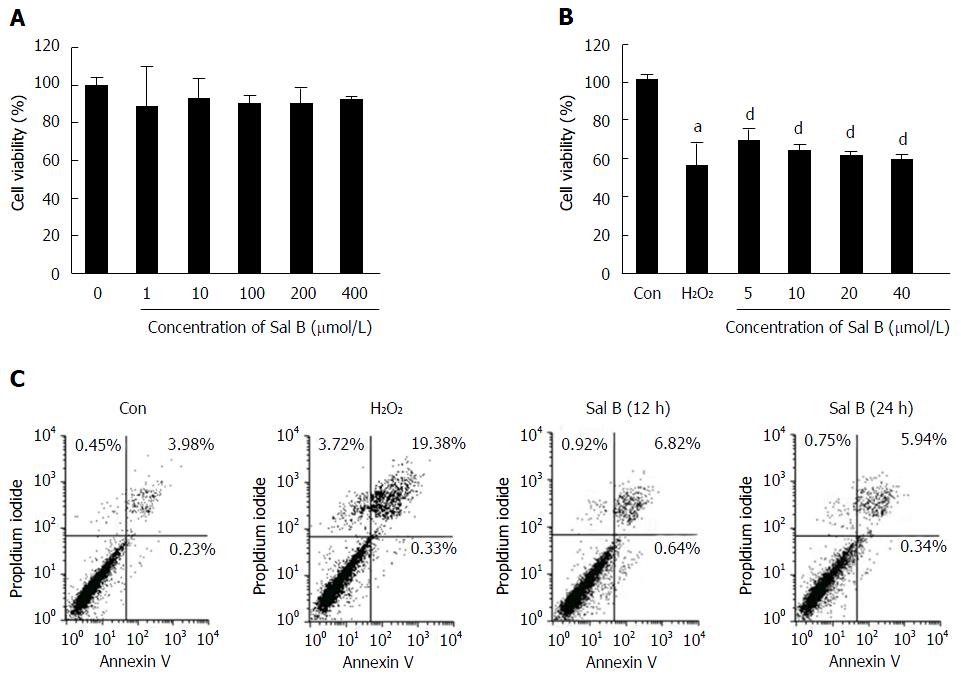
Figure 1 Effect of Sal B on apoptosis and death.
A: The viability of hepatocytes treated with different concentrations of Sal B for 24 h; B: The viability of hepatocytes treated with different concentrations of Sal B for 22 h following induction by H2O2 for 2 h; C: The Annexin V/PI assay with FACS. All data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test (aP < 0.05 vs Con; dP < 0.01 vs H2O2).
- Citation: Yan XF, Zhao P, Ma DY, Jiang YL, Luo JJ, Liu L, Wang XL. Salvianolic acid B protects hepatocytes from H2O2 injury by stabilizing the lysosomal membrane. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(29): 5333-5344
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i29/5333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5333