Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2017; 23(29): 5313-5323
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5313
Published online Aug 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5313
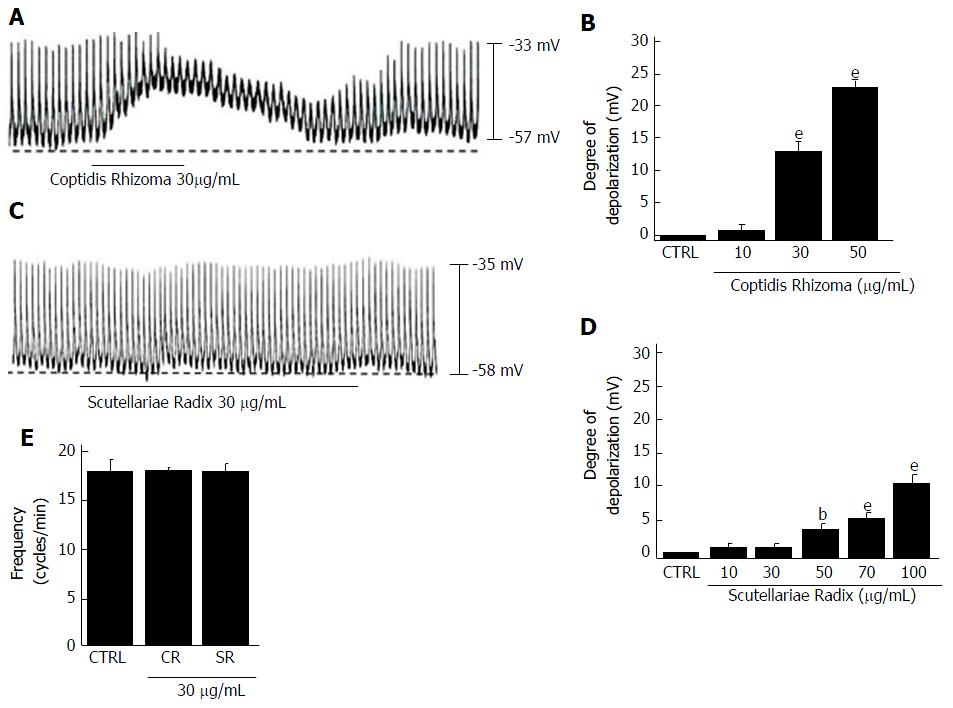
Figure 6 Effects of Coptidis Rhizoma and Scutellariae Radix on pacemaker potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine.
A: Pacemaking activities of ICCs exposed to Coptidis Rhizoma (30 μg/mL) in current-clamp mode (I = 0); B: Coptidis Rhizoma (10-50 μg/mL) concentration-dependently induced pacemaker potential depolarization. Responses to Coptidis Rhizoma are summarized; C: Pacemaking activities of ICCs exposed to Scutellariae Radix (30 μg/mL) in the current-clamp mode (I = 0); D: Scutellariae Radix (10-100 μg/mL) concentration-dependently induced pacemaker potential depolarization. Responses to Scutellariae Radix are summarized; E: Frequency changes to Coptidis Rhizoma and Scutellariae Radix are summarized. Bars represent the means ± SEMs. bP < 0.01 and eP < 0.001: Significantly different from the control. CTRL: Control; CR: Coptidis Rhizoma; SR: Scutellariae Radix; ICCs: Interstitial cells of Cajal.
- Citation: Kim HJ, Lee GS, Kim H, Kim BJ. Hwangryunhaedok-tang induces the depolarization of pacemaker potentials through 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors in cultured murine small intestine interstitial cells of Cajal. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(29): 5313-5323
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i29/5313.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5313