Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5246-5252
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5246
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5246
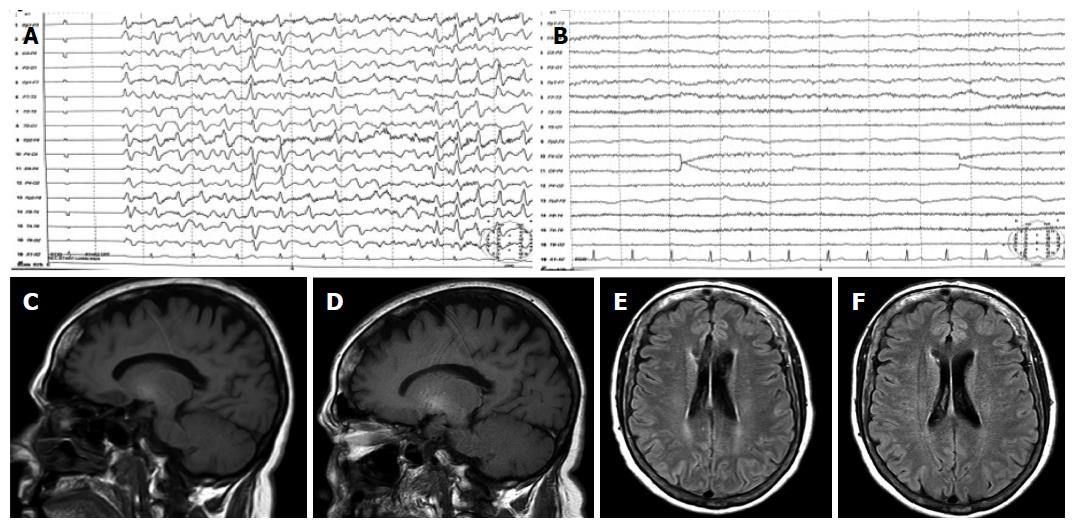
Figure 1 Electroencephalograph and magnetic resonance findings at baseline and after treatment with thyroid hormone.
A: EEG at baseline showing slow activity and generalized triphasic waves; B: EEG after treatment showing normalization of brain activity; C: T1-weighted MRI showed high-signal in basal ganglia at baseline; D: T1-weighted MRI performed after thyroid hormone replacement showed non-significant changes; E: FLAIR MRI sequence at baseline demonstrated subtle periventricular white matter hyperintensities; F: FLAIR MRI image after thyroid hormone replacement demonstrated a normalization of periventricular white matter signal abnormalities. EEG: Electroencephalograph; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Díaz-Fontenla F, Castillo-Pradillo M, Díaz-Gómez A, Ibañez-Samaniego L, Gancedo P, Guzmán-de-Villoria JA, Fernández-García P, Bañares-Cañizares R, García-Martínez R. Refractory hepatic encephalopathy in a patient with hypothyroidism: Another element in ammonia metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5246-5252
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5246.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5246