Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5167-5178
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5167
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5167
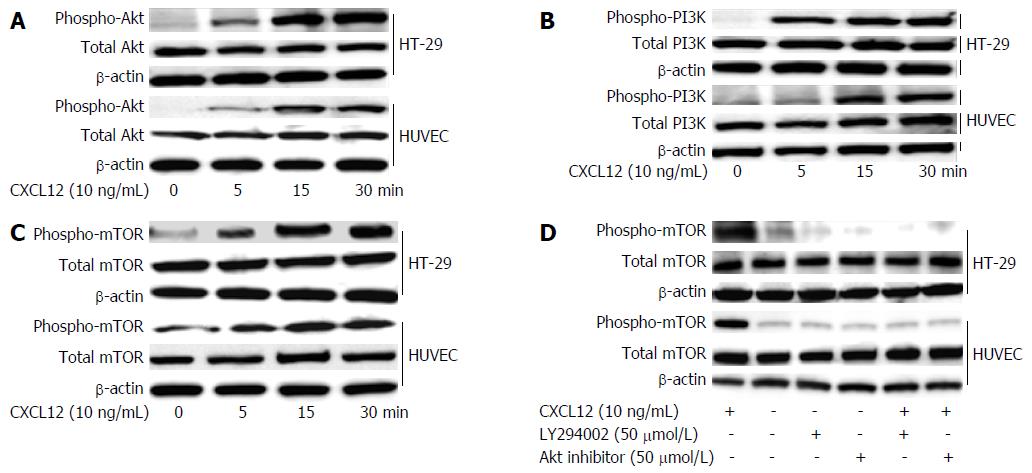
Figure 6 Stromal cell-derived factor-1-induced phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in colon cancer cell lines and stromal cells.
HT-29 cells and HUVECs were treated with 10 ng/mL of CXCL12 cultured for 5, 10 and 30 min. The cells were collected and lysed by lysis buffer. Aliquots of 30 μg of lysed protein were subjected to immunoblotting with a phospho-Akt (A), phospho-PI3K (B) and phosphor-mTOR (C) Abs. Detection of total Akt, PI3K or mTOR levels aided in loading control. HT-29 cells or HUVECs, after being pre-treated with 50 μmol/L Akt inhibitor and 50 μmol/L LY294002 for 1 h, were incubated with 10 ng/mL CXCL12 for 1 h. Results of immunoblotting using the mTOR Ab is shown (D). Detection of total mTOR levels served as loading control. Ab: Antibody; CXCL6: Granulocyte chemotactic protein-2; CXCL12: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cell.
- Citation: Ma JC, Sun XW, Su H, Chen Q, Guo TK, Li Y, Chen XC, Guo J, Gong ZQ, Zhao XD, Qi JB. Fibroblast-derived CXCL12/SDF-1α promotes CXCL6 secretion and co-operatively enhances metastatic potential through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5167-5178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5167.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5167