Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5158-5166
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5158
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5158
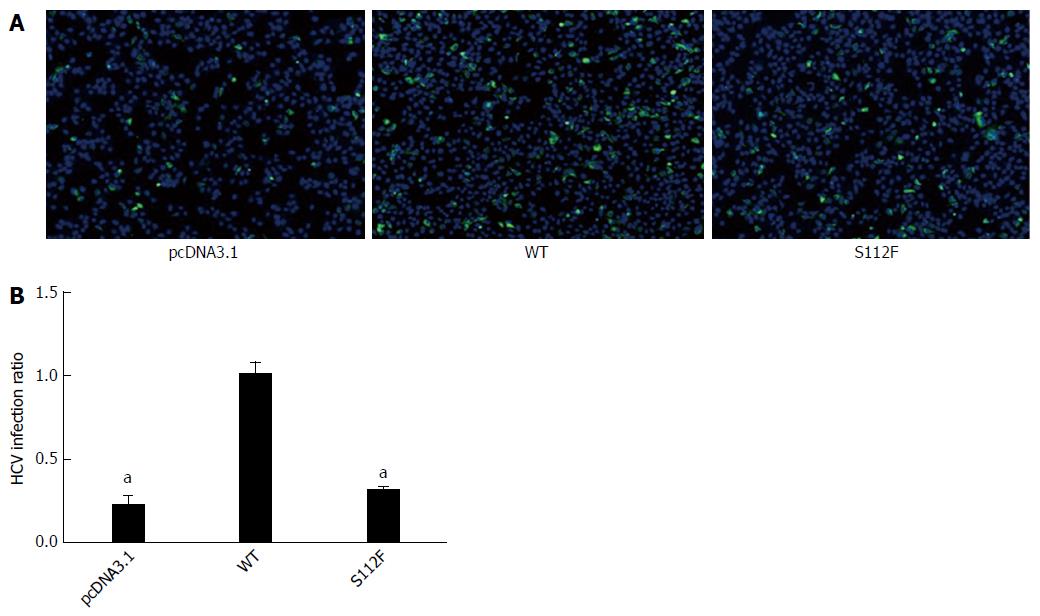
Figure 2 Effect of the class B scavenger receptor I single amino acid mutant on hepatitis C virus infectivity.
A: Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) of the effects of the SR-BI single amino acid mutant on hepatitis C virus (HCV) infectivity. Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in 96-well plates, cultured overnight, and then transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI (WT), or pcDNA- SR-BI/S112F. HCVcc (103 FFU/mL) was added 24 h after transfection, and the IFA was performed 48 h later. B: Effect of the SR-BI single amino acid mutant on the HCV viral RNA. Huh7-siSR-BI cells were seeded in 24-well plates, cultured overnight, and then transfected with pcDNA3.1 (NC), pcDNA-SR-BI, or pcDNA-SR-BI/S112F. HCVcc (104 FFU/mL) was added 24 h after transfection, and cells were harvested 72 h later to prepare RNA for the qRT-PCR analysis (aP < 0.05). SR-BI: Class B scavenger receptor I; WT: Wild type.
- Citation: Gao R, Gao W, Xu G, Xu J, Ren H. Single amino acid mutation of SR-BI decreases infectivity of hepatitis C virus derived from cell culture in a cell culture model. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5158-5166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5158