Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5146-5157
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146
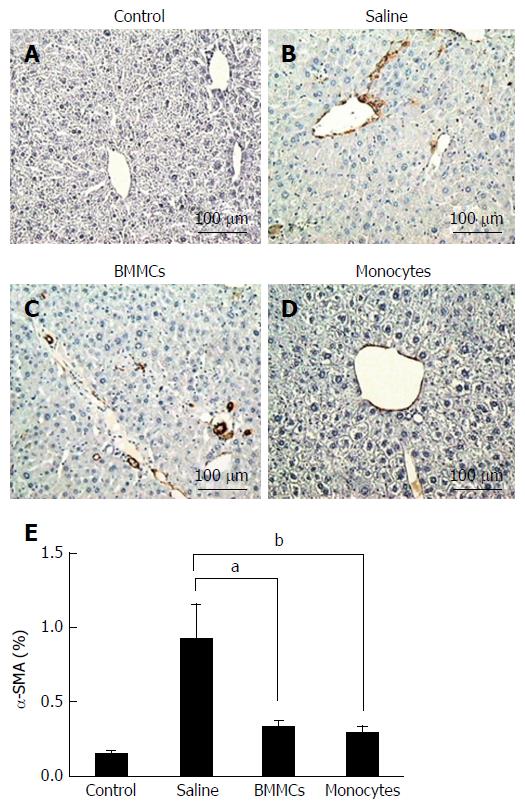
Figure 4 Immunohistochemistry for detection of α-SMA+ hepatic stellate cells in histological sections.
A-D: Control (A), saline-treated (B), BMMCs-treated (C) and CD11b+CD14+ monocyte-treated (D) groups of mice (magnification × 200); E: Measurement of α-SMA+ hepatic stellate cells at 2 mo after treatment with CD11b+CD14+ monocytes and BMMCs. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. BMMCs: Bone marrow mononuclear cells.
- Citation: de Souza VCA, Pereira TA, Teixeira VW, Carvalho H, de Castro MCAB, D’assunção CG, de Barros AF, Carvalho CL, de Lorena VMB, Costa VMA, Teixeira ÁAC, Figueiredo RCBQ, de Oliveira SA. Bone marrow-derived monocyte infusion improves hepatic fibrosis by decreasing osteopontin, TGF-β1, IL-13 and oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5146-5157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146