Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5146-5157
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146
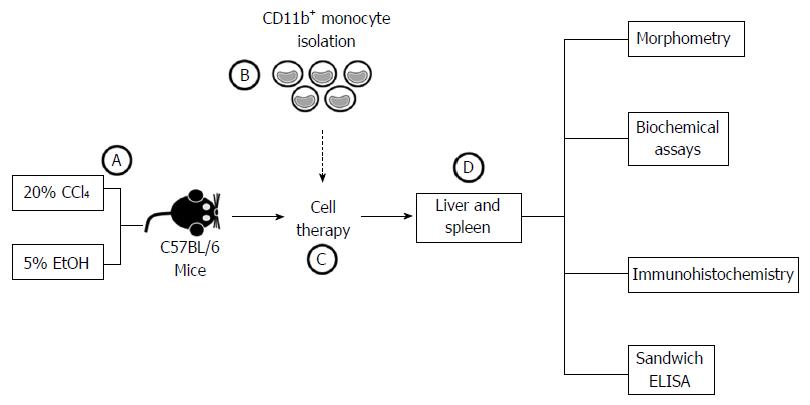
Figure 2 Schematic flowchart of experimental design.
A: Male C57BL/6 mice underwent chronic administration of CCl4 and EtOH solutions for 6 mo; B: Bone marrow mononuclear cells were harvested from C57BL/6 donor mice for CD11b+ monocyte isolation using immunomagnetic separation; C: Chronically liver-damaged mice underwent cell therapy; D: After 2 mo, effects of the treatment were evaluated using morphometric, biochemical, immunohistochemistry and sandwich ELISA analysis.
- Citation: de Souza VCA, Pereira TA, Teixeira VW, Carvalho H, de Castro MCAB, D’assunção CG, de Barros AF, Carvalho CL, de Lorena VMB, Costa VMA, Teixeira ÁAC, Figueiredo RCBQ, de Oliveira SA. Bone marrow-derived monocyte infusion improves hepatic fibrosis by decreasing osteopontin, TGF-β1, IL-13 and oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5146-5157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146