Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5115-5126
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5115
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5115
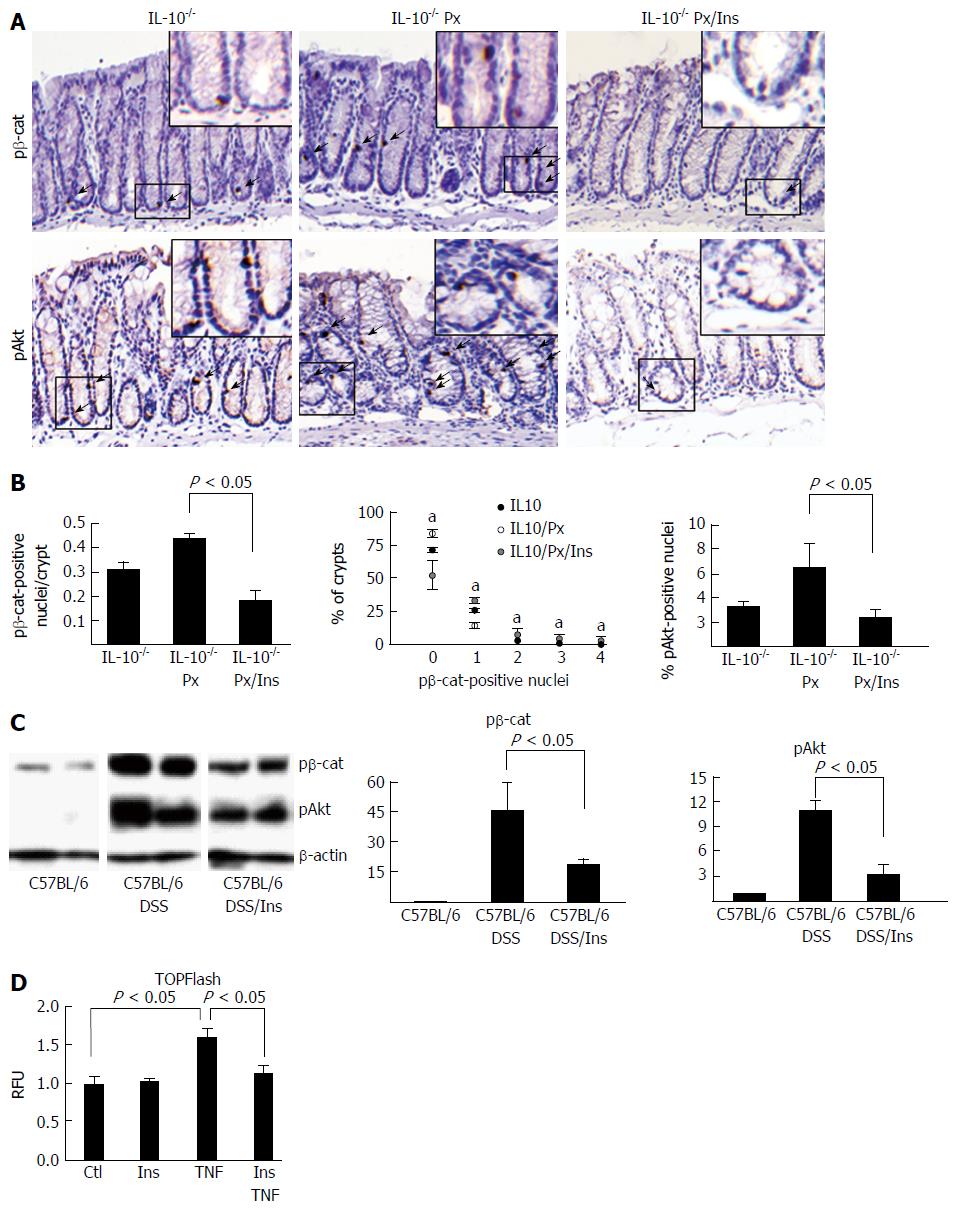
Figure 3 pβ-cat and pAkt are reduced in colitis mice treated with myo-inositol.
A: Representative images of pβ-cat and pAkt staining; B: Quantification of the number of pβ-cat- and pAkt-positive nuclei. Distribution of the percent of crypts containing 0-5 pβ-cat-positive nuclei. Values represent the mean ± SE, n = 4 mice in each group. aP < 0.05; C: Western blots of IEC showing levels of nuclear pβ-cat and pAkt in the 8 cycle model of DSS-induced colitis. Lanes were rearranged to be consistent with formatting. Densitometry was normalized to β-actin and presented as the fold change (mean ± SE). n = 2 control mice, 3 DSS-treated mice, and 3 DSS/myo-inositol-treated mice; D: TOPFlash reporter assay (shown in relative fluorescence units, RFU) for β-catenin activation in NCM460 cells treated with TNF or myo-inositol. n = 4 separate experiments.
- Citation: Bradford EM, Thompson CA, Goretsky T, Yang GY, Rodriguez LM, Li L, Barrett TA. Myo-inositol reduces β-catenin activation in colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5115-5126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5115