Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2017; 23(28): 5068-5085
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5068
Published online Jul 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5068
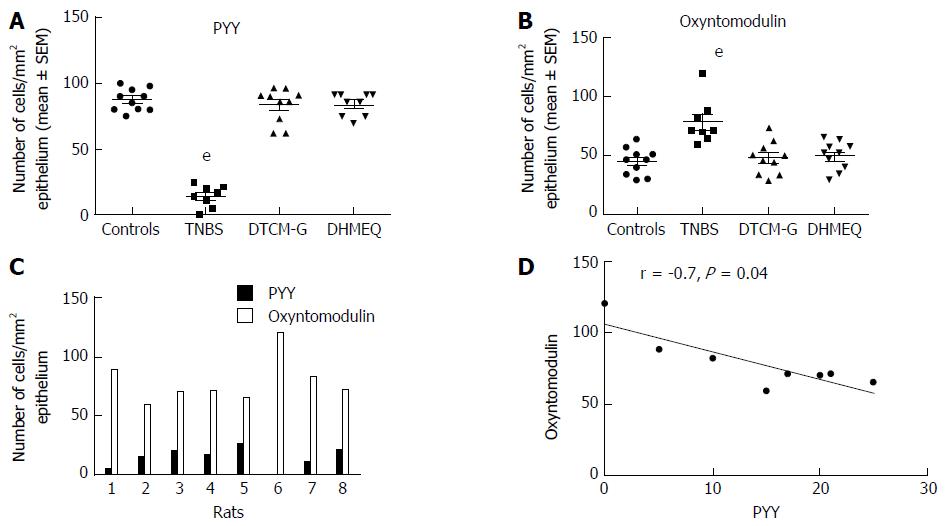
Figure 8 Colonic densities of (A) peptide YY-positive cells and (B) oxyntomodulin (enteroglucagon)-positive cells in control rats, in rats with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis, and in rats with TNBS-induced colitis treated with 3-[(dodecylthiocarbonyl)-methyl]-glutarimide (DTCM-G, an activator protein-1 inhibitor) and dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ, a nuclear factor-κB inhibitor).
Densities of PYY-positive and oxyntomodulin-positive cells in each rat of the TNBS group (C), and their correlation (D). eP < 0.001 vs controls. Reproduced from reference 274 with permission from the authors and the publisher. PYY: Peptide YY.
- Citation: El-Salhy M, Solomon T, Hausken T, Gilja OH, Hatlebakk JG. Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine peptides/amines in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(28): 5068-5085
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i28/5068.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5068