Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2017; 23(27): 4920-4934
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4920
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4920
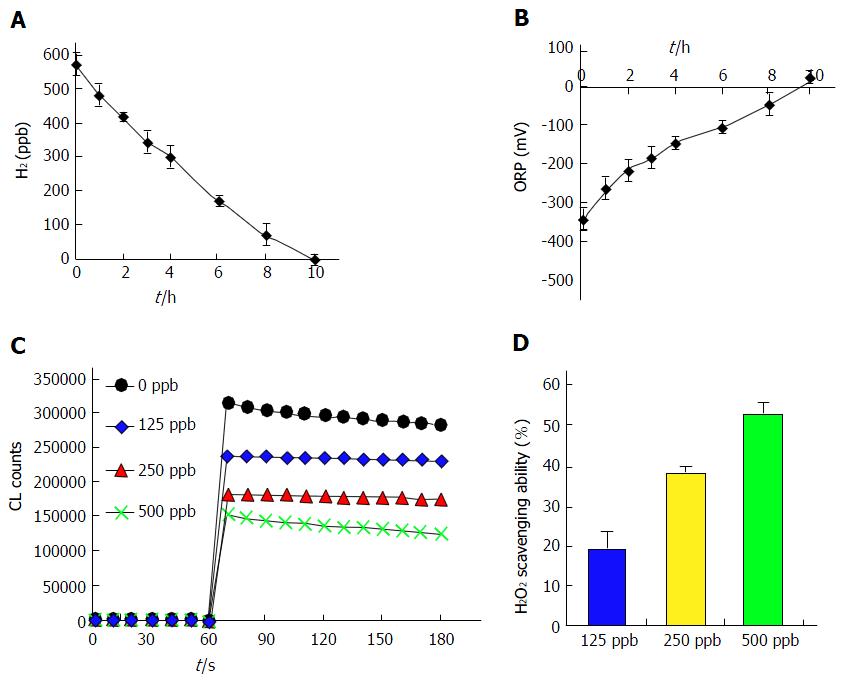
Figure 1 Scavenging of hydrogen peroxide by hydrogen-rich water in vitro.
A: The hydrogen content in HRW displayed a time-dependent decline and reach zero at 10 h when exposed to air; B: Accordingly, the values of ORP also rapidly returned to baseline at 10 h; C: Scavenging ROS ability measured with chemiluminescence emission by luminol. Values for chemiluminescence intensity were showed as counts for every 10 s in 180 s; D: ROS scavenging ability was calculated as averages from 60 to 180 s using the area under the curve. Values are expressed as means ± SD of three independent experiments. HRW: Hydrogen-rich water; ORP: Oxidation-reduction potential; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Lin CP, Chuang WC, Lu FJ, Chen CY. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of hydrogen-rich water alleviate ethanol-induced fatty liver in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(27): 4920-4934
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i27/4920.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4920