Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2017; 23(25): 4508-4516
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508
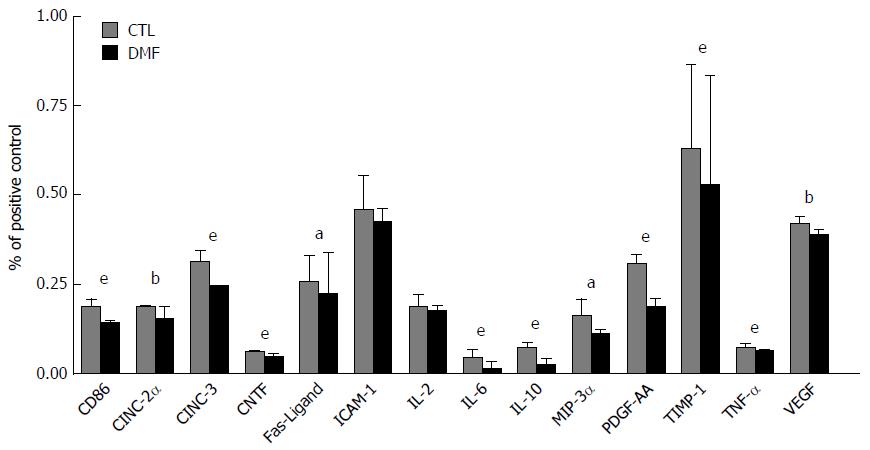
Figure 4 Inflammatory mediator production in rat serum.
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) significantly reduced the production of inflammatory mediators in the serum relative to the CTL group. Significant reductions of CD86, CINC-2α, CINC-3, CNTF, Fas ligand, IL-6, IL-10, MIP-3α, PDGF-AA, TIMP-1, TNF-α and VEGF were observed in the DMF-treated group. Data represent the mean ± SD (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001). DMF: Dimethyl fumarate; CTL: Control; IL: Interleukin; CD86: Cluster of differentiation 86; CINC-2α: Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-2α; CNTF: Ciliary neurotrophic factor; MIP-3α: Macrophage inflammatory protein-3α; PDGF-AA: Platelet-derived growth factor-AA; TIMP-1: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Takasu C, Vaziri ND, Li S, Robles L, Vo K, Takasu M, Pham C, Farzaneh SH, Shimada M, Stamos MJ, Ichii H. Treatment with dimethyl fumarate ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(25): 4508-4516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i25/4508.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508