Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2017; 23(25): 4508-4516
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508
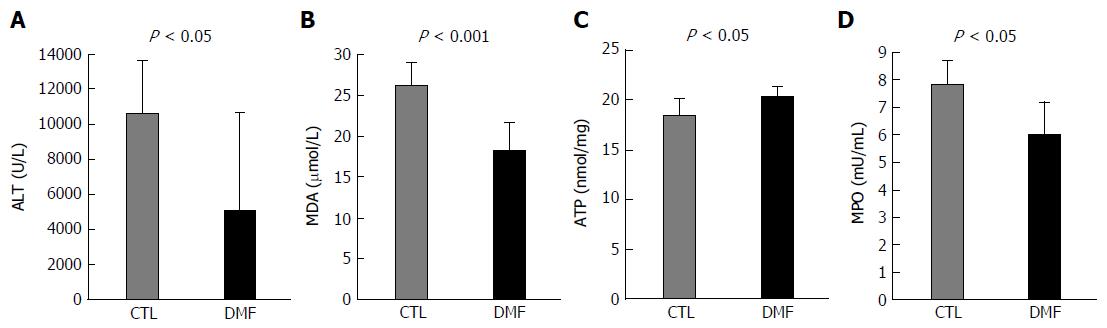
Figure 2 Effect of dimethyl fumarate on serum alanine aminotransferase and malondialdehyde and liver adenosine triphosphate and myeloperoxidase.
The levels of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (A) and malondialdehyde (MDA) (B) and liver adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (C) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) (C) in the liver tissue were determined. Serum ALT and MDA in the DMF group were significantly lower than in the CTL group (ALT: P < 0.05, MDA: P < 0.001; data represent the mean ± SD). Liver ATP in the DMF group was significantly higher than in the CTL group (P < 0.05; data represent the mean ± SD). Liver MPO in the DMF group was significantly lower than in the CTL group (P < 0.05; data represent the mean ± SD). DMF: Dimethyl fumarate; CTL: Control.
- Citation: Takasu C, Vaziri ND, Li S, Robles L, Vo K, Takasu M, Pham C, Farzaneh SH, Shimada M, Stamos MJ, Ichii H. Treatment with dimethyl fumarate ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(25): 4508-4516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i25/4508.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4508