Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2017; 23(25): 4491-4499
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4491
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4491
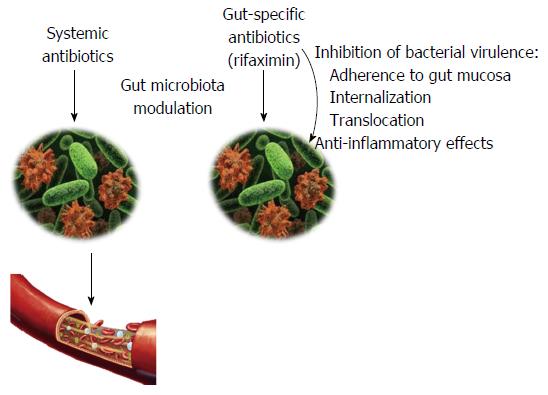
Figure 1 Effects of antibiotics on the gut microbiota.
Systemic antibiotics are mainly used to treat extra-intestinal infections but they indirectly affect the gut microbiota composition. Rifaximin is a poorly absorbed antibiotic, exerting its action exclusively in the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to the expected antimicrobial properties, rifaximin inhibits bacterial virulence, down-regulates inflammatory response and has the potential to positively modulate the composition of gut microbial community.
- Citation: Ponziani FR, Zocco MA, D’Aversa F, Pompili M, Gasbarrini A. Eubiotic properties of rifaximin: Disruption of the traditional concepts in gut microbiota modulation. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(25): 4491-4499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i25/4491.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4491