Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2017; 23(23): 4181-4190
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4181
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4181
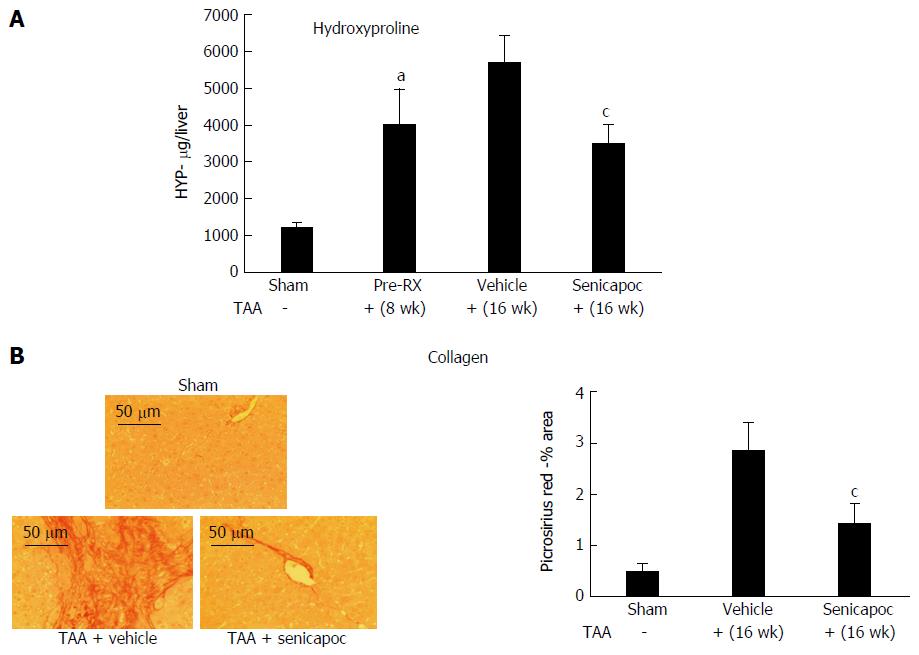
Figure 2 Senicapoc is anti-fibrotic in toxin-induced liver disease.
A: Eight weeks after administration of TAA, livers exhibited increased hydroxyproline (collagen) content (aP < 0.05 vs sham). Animals randomized to Senicapoc between weeks 8 and 16, exhibited reduced liver fibrosis at week 16 (cP < 0.05 vs TAA + vehicle). B: Picosirus red stained livers (20 ×) from representative sham, TAA + vehicle or TAA + Senicapoc-treated animals (16 wk TAA; 8 wk drug) are shown. Intervention with Senicapoc reduced hepatic collagen accumulation (cP < 0.05 vs TAA + vehicle).
- Citation: Paka L, Smith DE, Jung D, McCormack S, Zhou P, Duan B, Li JS, Shi J, Hao YJ, Jiang K, Yamin M, Goldberg ID, Narayan P. Anti-steatotic and anti-fibrotic effects of the KCa3.1 channel inhibitor, Senicapoc, in non-alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(23): 4181-4190
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i23/4181.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4181