Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2017; 23(23): 4158-4169
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4158
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4158
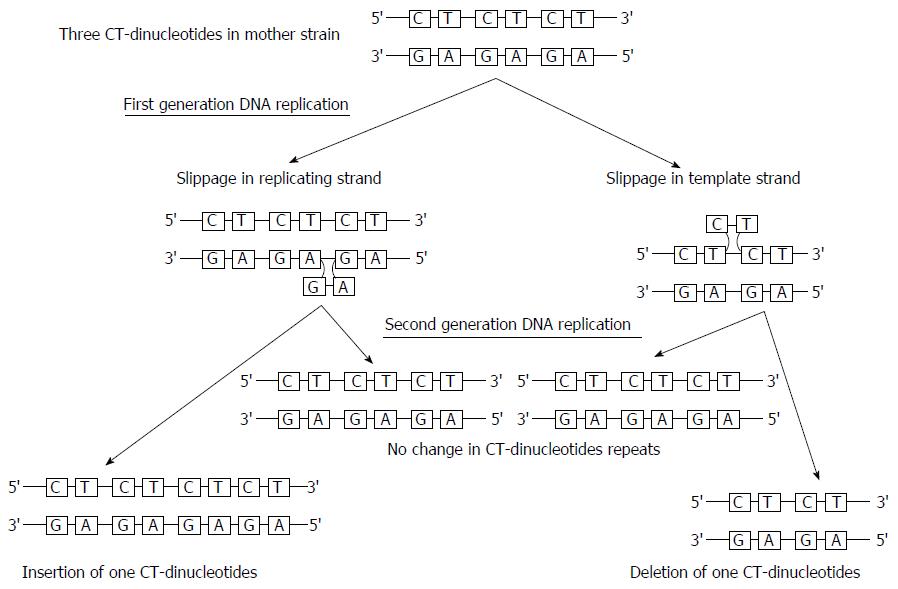
Figure 2 Cytosine-thiamidine-dinucleotide repeats and slipped strand mis-pairing.
Both replicating and template strands are prone to undergo for slippage mis-pairing. Slippage occurring in replicating strand during first generation of replication causes insertion of one CT-dinucleotide in replicating strand whereas the template strand contains original number of CT-dinucleotide. If slippage occurs in template strand during first generation replication, one CT-dinucleotide is deleted in replicating strand to make base paring. During second generation of DNA replication, out of two progeny generating from slippage in replicating strand, one progeny contains DNA with one CT-dinucleotide more than the mother strain while the other progeny contains same number of CT-dinucleotide as mother strain. During second generation of DNA replication, out of two progeny generating from slippage in template strand, one progeny contains DNA with one CT-dinucleotide less than the mother strain while other progeny contains DNA with same number of CT-dinucleotide as do mother strain. CT: Cytosine-thiamidine.
- Citation: Ansari S, Yamaoka Y. Helicobacter pylori BabA in adaptation for gastric colonization. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(23): 4158-4169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i23/4158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4158