Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2017; 23(22): 4007-4015
Published online Jun 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4007
Published online Jun 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4007
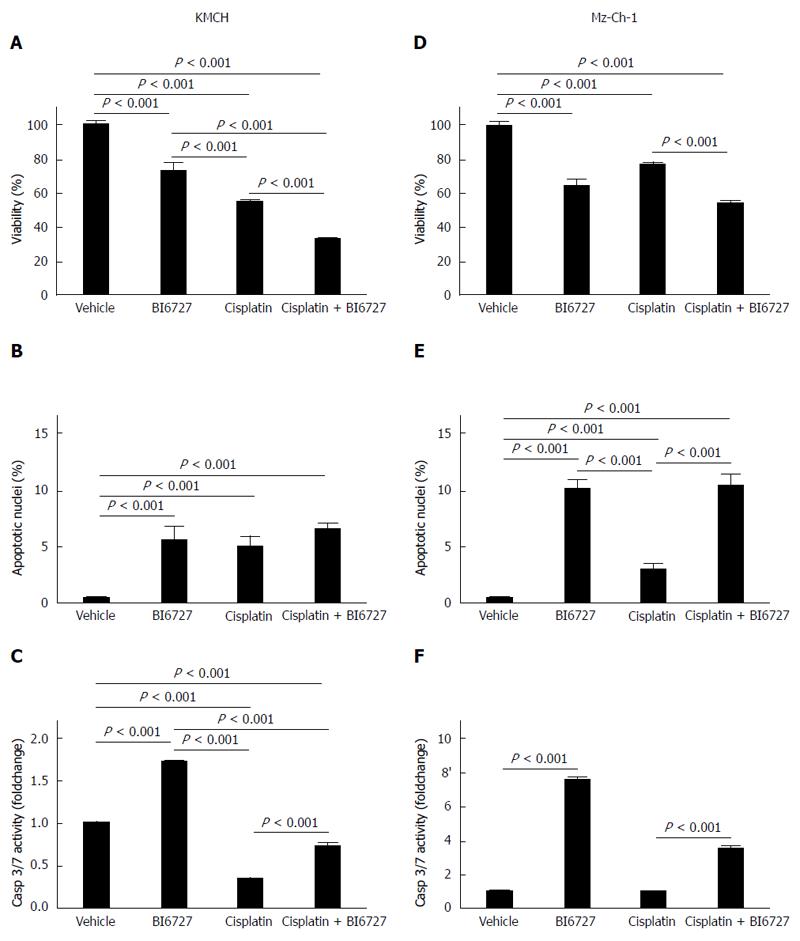
Figure 1 PLK-inhibitor BI6727 reduces cell viability and acts pro apoptotic in cholangiocellular carcinoma cell lines.
Cell viability of CCA cell lines KMCH-1 (A) and Mz-Ch-1 (D) treated with the PLK-inhibitor BI6727 (200 nmol/L for 24 h), the cytostatic drug cisplatin (1 mmol/L for 24 h) or both components was assessed by MTT assay (A, D) shown as % of viable cells (viability) compared to vehicle-treated cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3). Apoptotic nuclei were determined in DAPI stained KMCH (B) and Mz-Ch-1 (E) cells after treatment using fluorescence microscopy. The number of apoptotic nuclei was normalized to the total number of nuclei (mean ± SEM, n = 4). Apoptosis induction in KMCH-1 (C) and Mz-Ch-1 (F) cells was measured by fluorescent Caspase-3/-7 activity assay shown as foldchange of vehicle-treated cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3). PLK: Polo-like kinase; CCA: Cholangiocarcinoma; MTT: 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromid; DAPI: 4’, 6-diamino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride.
- Citation: Sydor S, Jafoui S, Wingerter L, Swoboda S, Mertens JC, Gerken G, Canbay A, Paul A, Fingas CD. Bcl-2 degradation is an additional pro-apoptotic effect of polo-like kinase inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(22): 4007-4015
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i22/4007.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.4007