Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2017; 23(21): 3934-3944
Published online Jun 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3934
Published online Jun 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3934
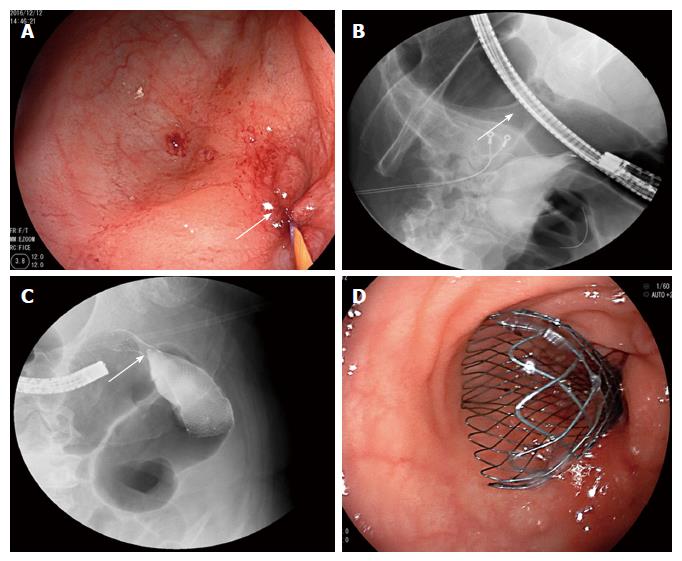
Figure 7 Stent placement for sigmoid colon stenosis.
The patient underwent stent placement for sigmoid colon stenosis. A guide wire was inserted via electronic colonoscopy to the proximal end of the stenotic segment (arrow, A). X-ray radiography confirmed that the guide wire had achieved the correct position and showed that the stenotic segment was 4 cm long (arrow, B). Additionally, X-ray showed that an 8-cm-long self-expandable memory metallic stent had been placed at the correct location (arrow, C). Colonoscopy confirmed that the distal end of the stent was at the correct location (D).
- Citation: Zhang ZM, Lin XC, Ma L, Jin AQ, Lin FC, Liu Z, Liu LM, Zhang C, Zhang N, Huo LJ, Jiang XL, Kang F, Qin HJ, Li QY, Yu HW, Deng H, Zhu MW, Liu ZX, Wan BJ, Yang HY, Liao JH, Luo X, Li YW, Wei WP, Song MM, Zhao Y, Shi XY, Lu ZH. Ischemic or toxic injury: A challenging diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced stenosis of the sigmoid colon. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(21): 3934-3944
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i21/3934.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3934