Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2017; 23(21): 3805-3814
Published online Jun 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3805
Published online Jun 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3805
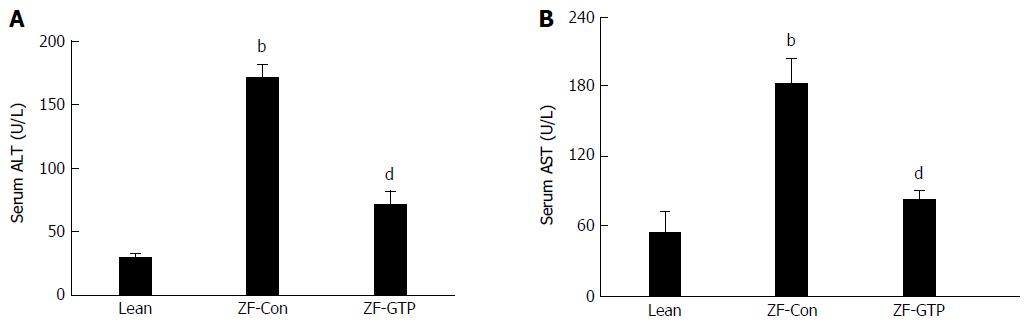
Figure 1 Effect of green tea polyphenols on alanine transaminase (A) and aspartate transaminase (B) in high-fat diet Zucker fatty rats.
Serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) concentrations were measured after 8 wk of daily treatment with saline (5 mL/kg; Lean, ZF-Con) or GTP (200 mg/kg; ZF-GTP). Data are means ± SEM, n = 12 rats/group. bP < 0.01 vs Lean rats and dP < 0.01 vs ZF-Con rats.
- Citation: Tan Y, Kim J, Cheng J, Ong M, Lao WG, Jin XL, Lin YG, Xiao L, Zhu XQ, Qu XQ. Green tea polyphenols ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through upregulating AMPK activation in high fat fed Zucker fatty rats. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(21): 3805-3814
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i21/3805.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3805