Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2017; 23(20): 3607-3614
Published online May 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3607
Published online May 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3607
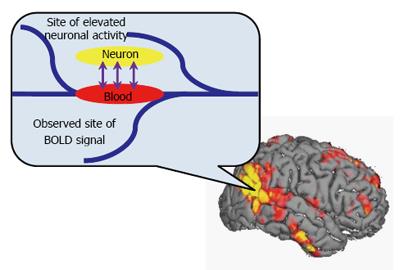
Figure 2 Mechanism of blood oxygenation level dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging.
BOLD-fMRI functions by detecting a local increase in relative blood oxygenation resulting from neurotransmitter activity and reflecting local neuronal firing rates. The nervous system activity is detected indirectly by assaying the proportion between deoxyhemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin in blood. BOLD-fMRI: Blood oxygenation level dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Lv K, Fan YH, Xu L, Xu MS. Brain changes detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in patients with Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(20): 3607-3614
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i20/3607.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3607