Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2017; 23(20): 3607-3614
Published online May 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3607
Published online May 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3607
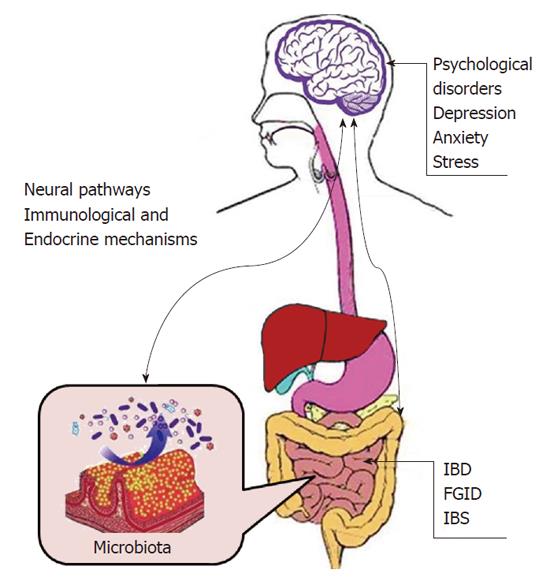
Figure 1 Brain-gut-enteric microbiota axis.
The bidirectional brain-gut-enteric microbiota axis between the brain and gut involves neural pathways, immunological and endocrine mechanisms, and it is closely associated with microbiota and psychological disorders such as depression, anxiety and stress. These disorders may result in FGID, IBD and IBS. FGID: Functional gastrointestinal disorders; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Citation: Lv K, Fan YH, Xu L, Xu MS. Brain changes detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in patients with Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(20): 3607-3614
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i20/3607.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3607