Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2017; 23(2): 275-285
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.275
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.275
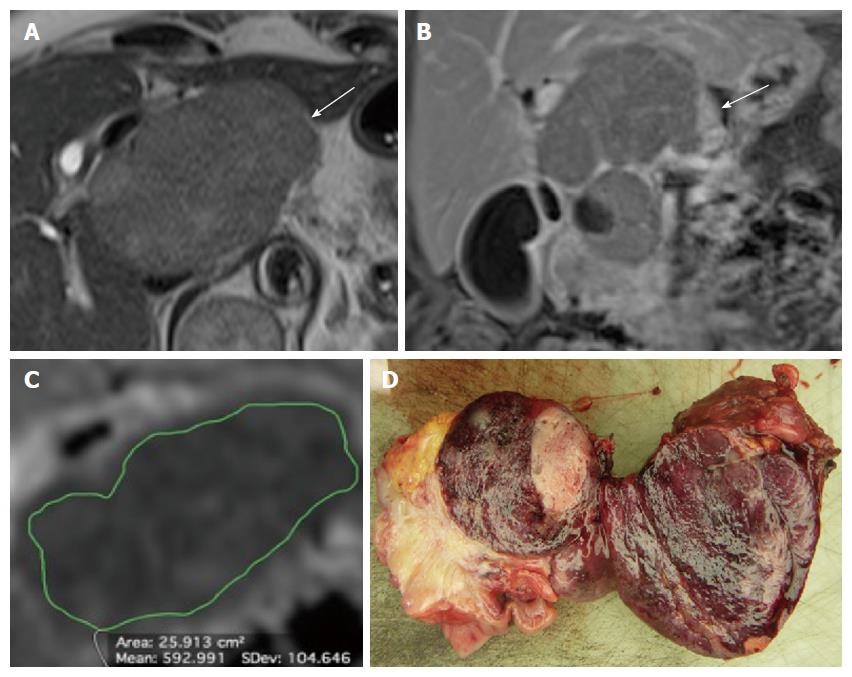
Figure 3 Non-hyperfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm of the pancreatic head classified as G3, stage 3b tumor at histology (Ki67 60%, T4, N1, M0) in a 76 years-old woman.
A: Axial T2-weighted half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin echo (HASTE) image (TR/TE, ∞/90) shows a large, slightly hyperintense tumor in the pancreatic head (arrow); B: On coronal fat-saturated T1-weighted volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (VIBE) gradient echo image (TR/TE 3.5/1.3 ms) acquired during the delayed phase of the dynamic study the tumor shows heterogeneous contrast enhancement (arrow); C: At quantitative analysis of ADC map the tumor shows low mean ADC value; D: The surgical specimen (pancreaticoduodenectomy, sagittal cut) shows a large lesion of the pancreatic head with heterogeneous aspect.
- Citation: De Robertis R, Cingarlini S, Tinazzi Martini P, Ortolani S, Butturini G, Landoni L, Regi P, Girelli R, Capelli P, Gobbo S, Tortora G, Scarpa A, Pederzoli P, D’Onofrio M. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: Magnetic resonance imaging features according to grade and stage. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(2): 275-285
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i2/275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.275