Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2017; 23(2): 242-255
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242
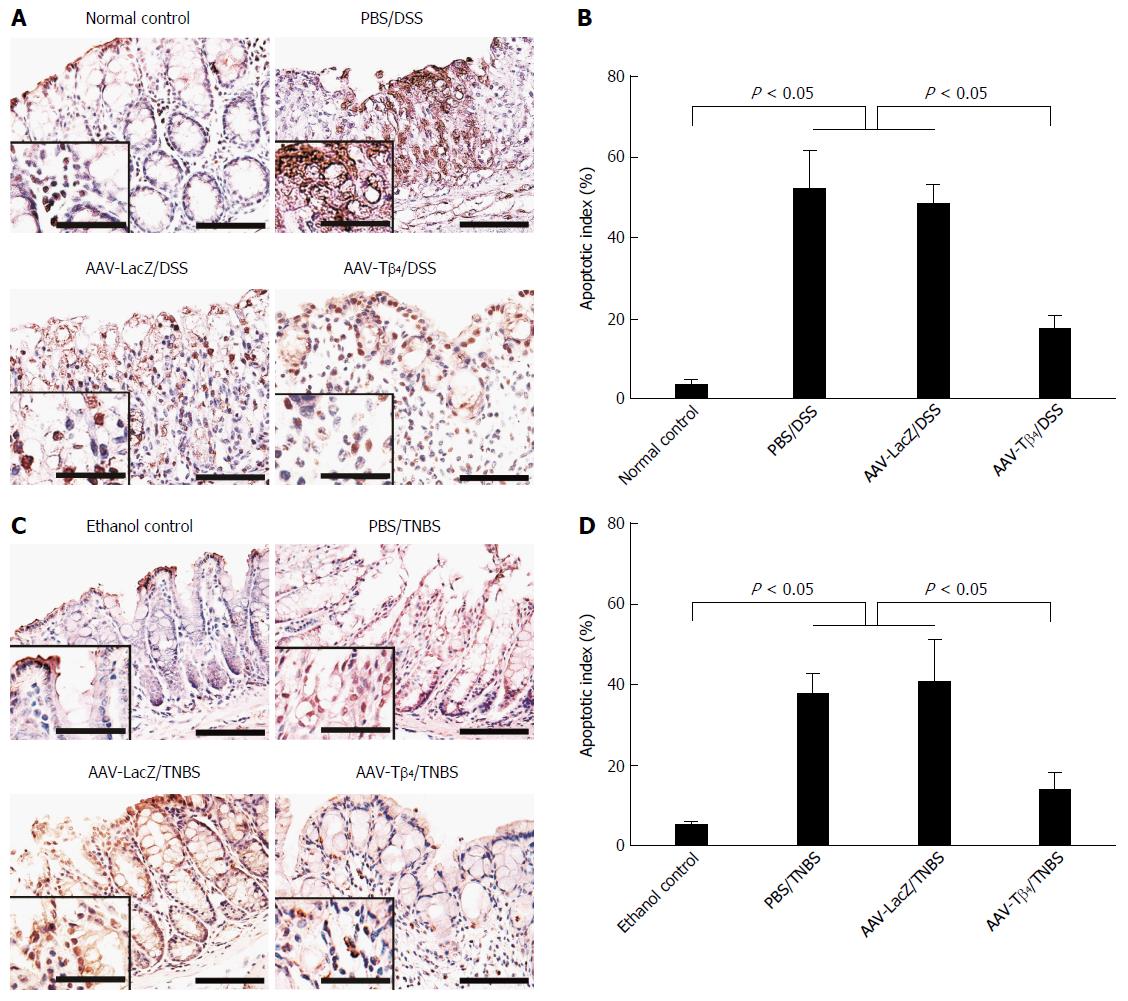
Figure 5 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 alleviated dextran sulfate sodium- and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced epithelial cell apoptosis in the colonic mucosa.
TUNEL staining showed that intracolonic adeno-associated virus (AAV)-thymosin β4 (Tβ4) prevented the colonic mucosal epithelia from undergoing apoptosis and thus led to decreased apoptotic indexes (AIs) in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)- (A and B) and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced (C and D) colitis in mice. The insets indicate the TUNEL-positive nuclear staining. Error bars indicate the SD. Scale bar: 50 μm and 25 μm (insets).
- Citation: Zheng XY, Lv YF, Li S, Li Q, Zhang QN, Zhang XT, Hao ZM. Recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 suppresses experimental colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(2): 242-255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i2/242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242