Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2017; 23(2): 242-255
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242
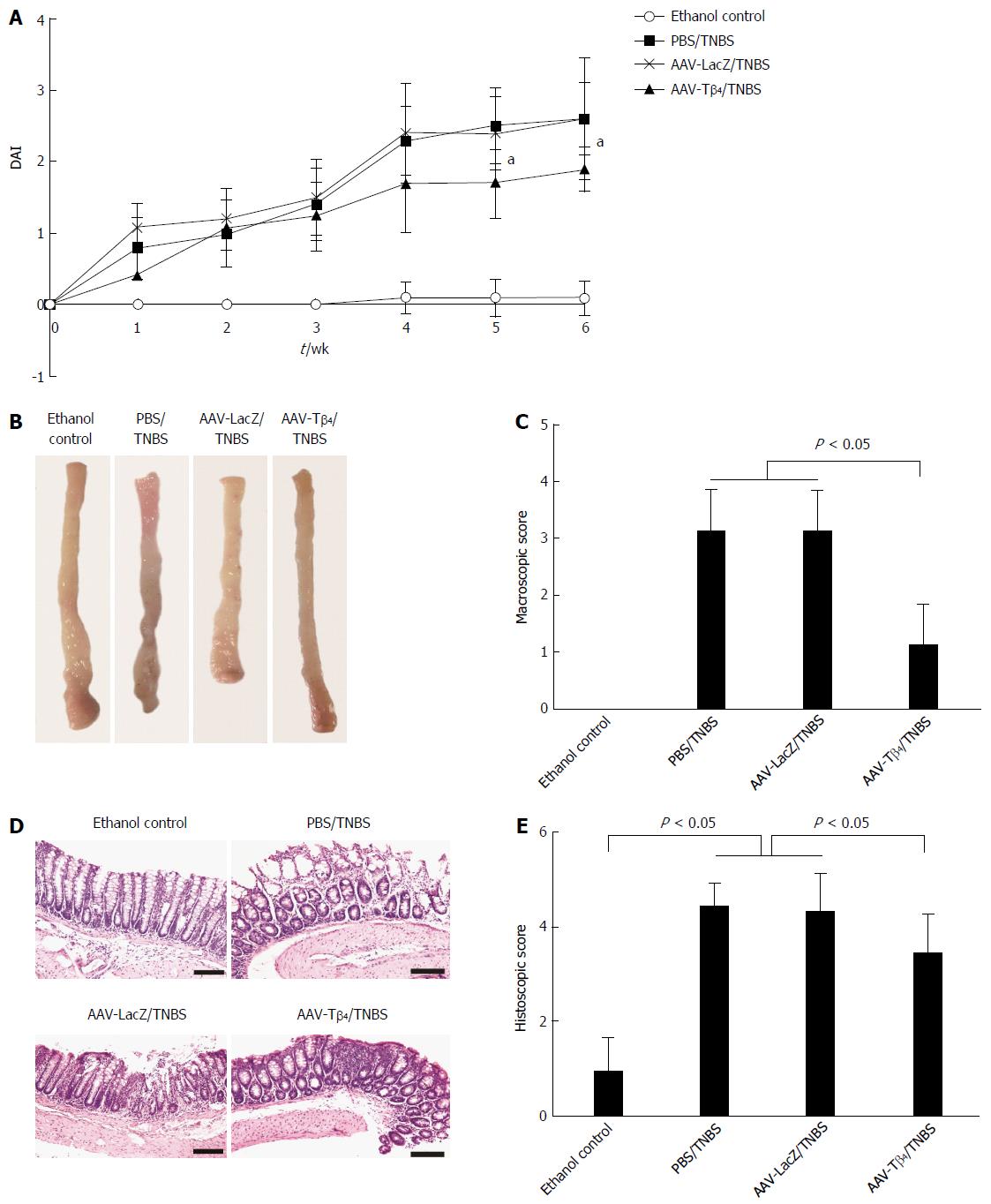
Figure 3 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 improved 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice.
A: Dynamic changes in DAI [the asterisk indicates aP < 0.05 vs PBS/2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) or adeno-associated virus (AAV)-LacZ/TNBS group]; B: TNBS treatment resulted in hyperemia, edema and ulceration, which were attenuated by Tβ4; C: Macroscopic score of AAV-Tβ4/TNBS group was significantly lower than those of the other two TNBS groups; D and E: Histological observation of colonic tissue (HE staining, magnification × 200) showed that AAV-Tβ4 relieved TNBS-induced colonic mucosal lesions and reduced the histological score. Error bars indicate the SD. Scale bars = 50 μm. DAI: Disease activity index.
- Citation: Zheng XY, Lv YF, Li S, Li Q, Zhang QN, Zhang XT, Hao ZM. Recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 suppresses experimental colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(2): 242-255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i2/242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242