Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2017; 23(18): 3240-3251
Published online May 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3240
Published online May 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3240
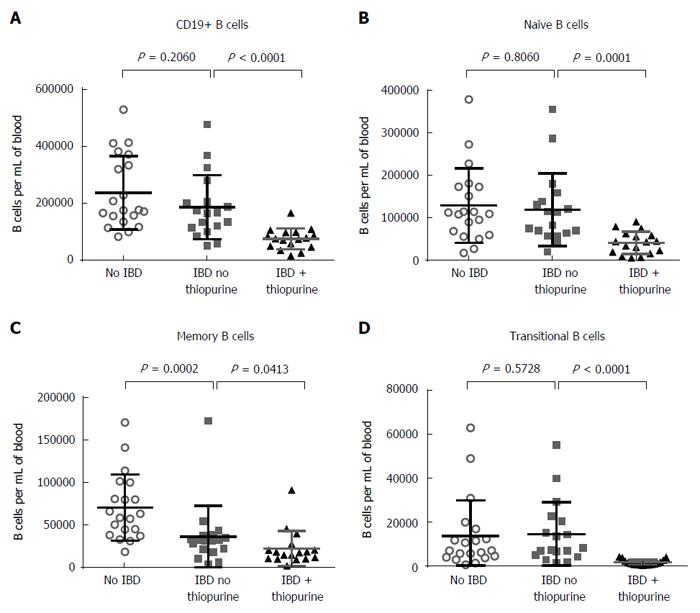
Figure 4 Thiopurine-associated lymphopenia is due to decreased B cells.
CD3-, CD19+ B cell (A) counts per ml of blood were compared between cohorts, as were CD19+, CD27-, IgD+, CD38- naïve B cells (B), CD19+, CD27+, IgD-, CD20+, CD38- memory B cells (C), and CD19+, CD27-, IgD+, CD38+ transitional B cells (D). P values reflect two-tailed Mann-Whitney non-parametric comparisons.
- Citation: Lord JD, Shows DM. Thiopurine use associated with reduced B and natural killer cells in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(18): 3240-3251
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i18/3240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i18.3240