Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2017; 23(16): 2899-2911
Published online Apr 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2899
Published online Apr 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2899
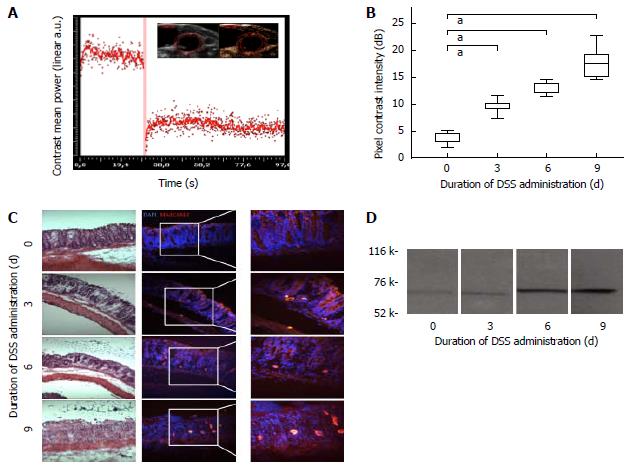
Figure 3 mucosal addressin cellular adhesion molecule-1-targeted contrast enhanced ultrasound reflects experimental intestinal inflammation.
A: Schematic illustration of a destruction-replenishment sequence with ultrasound pulses of high acoustic power (red bar) and reperfusion of contrast agent for acquisition of highly specific molecularly targeted CEUS. Image insert showing B mode image (left) and corresponding CEUS image (right); B: CEUS with targeted contrast agent against MAdCAM-1. Contrast mean power of defined ROI in descending colon in arbitrary unit dB. Decibel values correlate with exposure to DSS in a time-dependent manner. Boxplot with median and whiskers, n = 10 for each group, aP < 0.05; C: Immunofluorescence with staining against MAdCAM-1 (bright red), cell nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue). Positively stained cells were counted in at least 10 representative high power fields per section and cell numbers were expressed semi-quantitatively. Left panel: corresponding HE stained sections; D: Immunoblot with purified anti-mouse MAdCAM-1 antibody showing a characteristic protein band at 58-66kDa. Animals exposed to DSS for 6 and 9 d showing stronger expression of MAdCAM-1 than control animals. DSS: Dextran sodium-sulfate; CEUS: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; MAdCAM-1: Mucosal addressin cellular adhesion molecule-1.
- Citation: Brückner M, Heidemann J, Nowacki TM, Cordes F, Stypmann J, Lenz P, Gohar F, Lügering A, Bettenworth D. Detection and characterization of murine colitis and carcinogenesis by molecularly targeted contrast-enhanced ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(16): 2899-2911
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i16/2899.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2899