Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2017; 23(15): 2785-2794
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2785
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2785
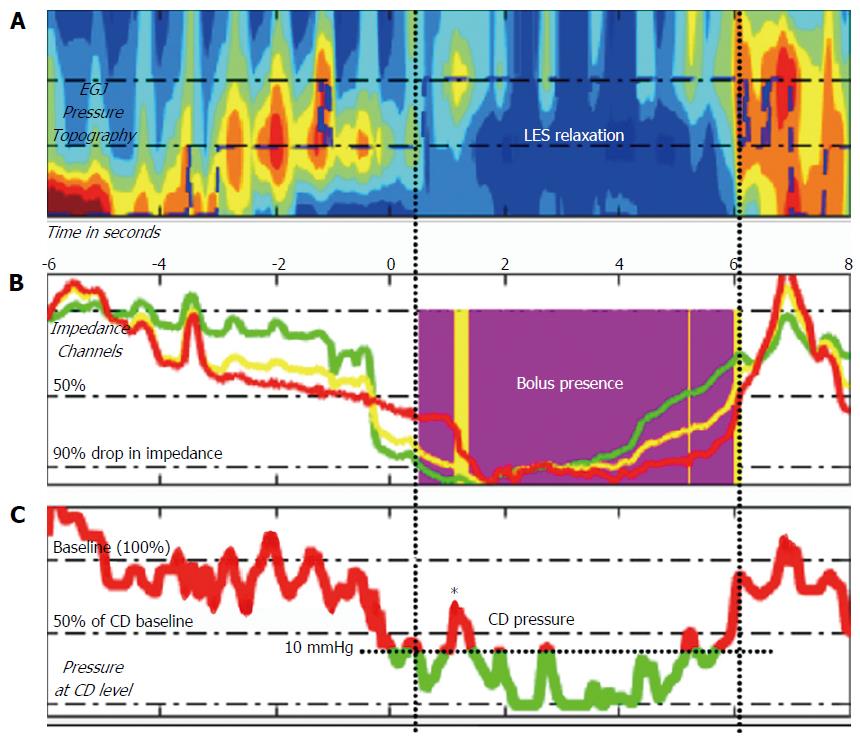
Figure 2 Method for determining bolus flow time at the esophagogastric junction using pressure impedance data (modified from Lin 2014).
A: Esophageal pressure topography of region of interest at EGJ; B: Bolus flow is determined as occurring at the EGJ when the distal esophageal impedance drops below 90% of baseline until impedance returns above 50% baseline (purple area), provided pressure criteria are simultaneously met at the crural diaphragm (CD) position; C: Pressure above 10 mmHg and 50% peak pressure inhibits bolus flow at CD position despite impedance criteria being met (* - corresponding with yellow area in B).
- Citation: Cock C, Besanko LK, Burgstad CM, Thompson A, Kritas S, Heddle R, Fraser RJ, Omari TI. Age-related impairment of esophagogastric junction relaxation and bolus flow time. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(15): 2785-2794
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i15/2785.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2785