Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2017; 23(15): 2785-2794
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2785
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2785
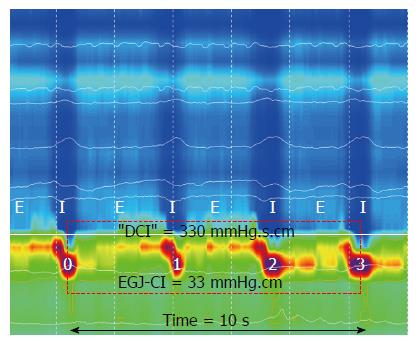
Figure 1 Method for determining esophagogastric junction contractile integral.
Inspiration (I) and expiration (E) are pictured for the intra thoracic portion above the EGJ (respiratory inversion pictured as dotted white line). Isobaric contour tool is adjusted to 2 mmHg above the intra gastric pressure to determine the boundaries for the EGJ. The “DCI box” (dotted red) is placed around the EGJ starting at the diaphragmatic contraction (mid-point inspiration) and extended for 3 further respiratory cycles. The “DCI”-value is then divided by time to determine EGJ-CI in mmHg.cm. EGJ: Esophagogastric junction.
- Citation: Cock C, Besanko LK, Burgstad CM, Thompson A, Kritas S, Heddle R, Fraser RJ, Omari TI. Age-related impairment of esophagogastric junction relaxation and bolus flow time. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(15): 2785-2794
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i15/2785.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2785