Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2017; 23(15): 2651-2659
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2651
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2651
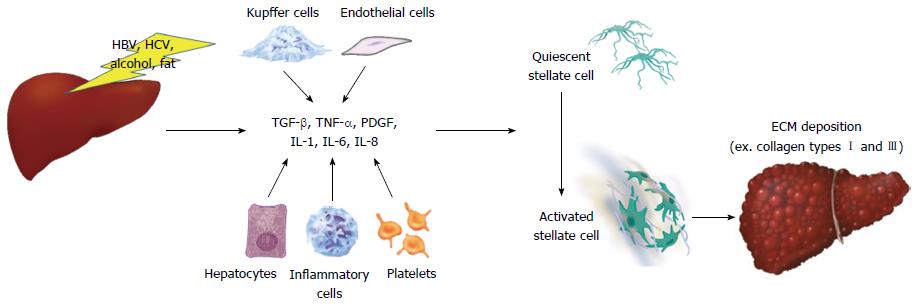
Figure 1 The mechanisms of activation of hepatic stellate cells during chronic liver injury, resulting in synthesis of excess extracellular matrix.
Once chronic liver injury has occurred, damaged hepatocytes, activated sinusoidal cells, platelets, and recruited inflammatory cells release various profibrogenic cytokines, which activate hepatic stellate cells, resulting in synthesis of excess extracellular matrix, such as type I and type III collagens. ECM: Extracellular matrix; IL: Interleukin; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Iida-Ueno A, Enomoto M, Tamori A, Kawada N. Hepatitis B virus infection and alcohol consumption. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(15): 2651-2659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i15/2651.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2651