Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2017; 23(13): 2414-2423
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2414
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2414
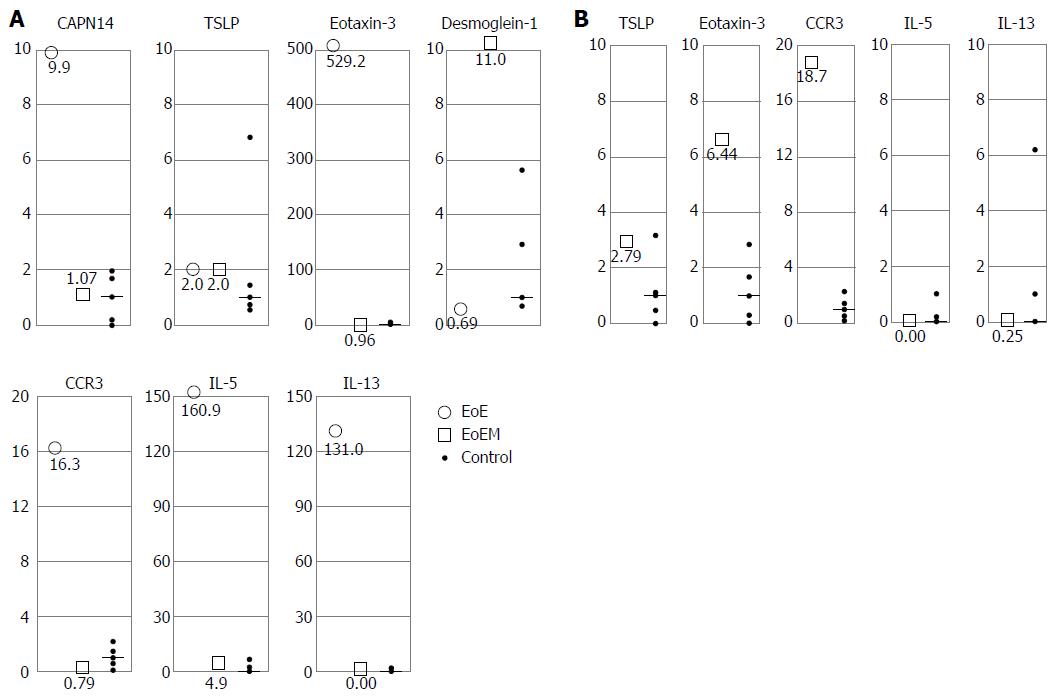
Figure 5 Real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis for esophageal mucosal and muscle layer samples (a vertical axis scale indicates the relative ratio compared with median control value converted to 1).
A: mRNA analysis for esophageal mucosal specimens in eosinophilic esophagitis (○), and eosinophilic esophageal myositis (□). In cases 1, 3, 4, and 5 with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), the expression of CAPN14, eotaxin-3, CCR3, IL-5, and IL-13 was increased, while the expression of DSG1 was decreased. In cases of eosinophilic esophageal myositis (case 9, and 10), no change was observed in CAPN14, TSLP, eotaxin-3, CCR3, IL-5, and IL-13 expression levels. The expression level of DSG1 was highly preserved in EoEM; B: mRNA analysis for esophageal muscle specimens in eosinophilic esophageal myositis (□). In eosinophilic esophageal myositis (case 9 and 10), muscle-layer samples by peroral esophageal muscle biopsy were also sent for mRNA expression analysis. The levels of eotaxin-3 and CCR3 were increased, although TSLP, IL-5, and IL-13 were within control value ranges.
- Citation: Sato H, Nakajima N, Takahashi K, Hasegawa G, Mizuno KI, Hashimoto S, Ikarashi S, Hayashi K, Honda Y, Yokoyama J, Sato Y, Terai S. Proposed criteria to differentiate heterogeneous eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders of the esophagus, including eosinophilic esophageal myositis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(13): 2414-2423
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i13/2414.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2414