Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2017; 23(13): 2414-2423
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2414
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2414
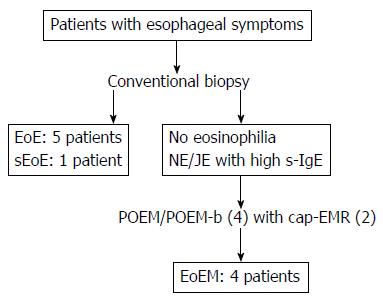
Figure 1 The schema of the present study.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) was diagnosed by conventional endoscopy in 5 patients, and a subtype of eosinophilic esophagitis (subepithelial eosinophilic esophagitis: sEoE) in 1 patient. Patients with no eosinophilia by conventional biopsy and with a nutcracker esophagus (NE) or jackhammer esophagus (JE) identified on high-resolution manometry received peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). These patients also showed elevated serum immunoglobulin E (s-IgE) levels. Four patients were diagnosed with eosinophilic esophageal myositis (EoEM) by peroral esophageal muscle biopsy (POEM-b), with cap-fitted endoscopic mucosal resection used in two of these four patients to facilitate POEM/POEM-b entry.
- Citation: Sato H, Nakajima N, Takahashi K, Hasegawa G, Mizuno KI, Hashimoto S, Ikarashi S, Hayashi K, Honda Y, Yokoyama J, Sato Y, Terai S. Proposed criteria to differentiate heterogeneous eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders of the esophagus, including eosinophilic esophageal myositis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(13): 2414-2423
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i13/2414.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2414